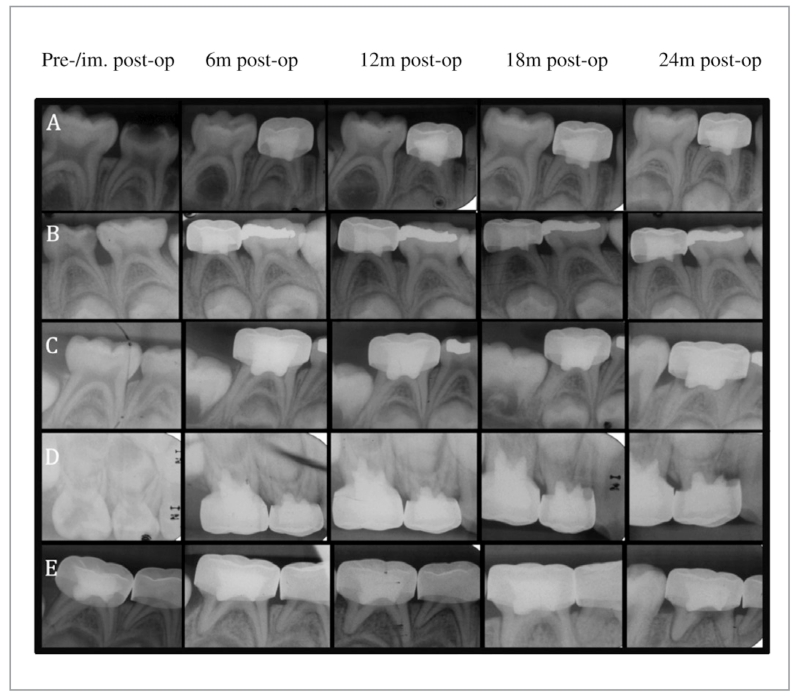
Figure 2.
Representative periapical radiographs depicting outcomes of pulpotomies: (A) Gray mineral trioxide aggregate-treated tooth (no. S) showing progressive dentin bridge formation and pulpal canal obliteration (mesial and distal canal); (B) Diluted formocresol-treated tooth (no. L) showing progressive pulp canal obliteration (mesial and distal canal); (C) Diluted formocresol-treated tooth (no. T) showing progressive internal root resorption (distal canal); (D) Diluted formocresol-treated tooth (no. B) showing progressive internal root resorption-perforated to external root resorption (mesial canal); and (E) Diluted formocresol-treated tooth (no. T) showing progressive widening of the periodontal ligament space and a periradicular lesion (mesial and distal canal).