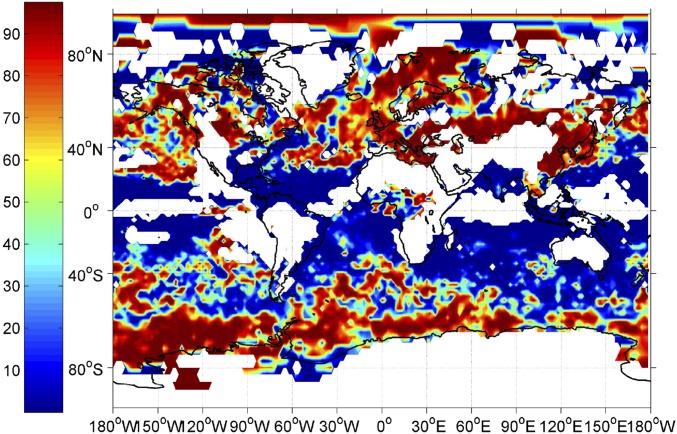
Fig. 2.
Percent contribution of vertical velocity variation to the temporal variability in activated cloud droplet number concentration (per cubic centimeter) for all clouds at the 825-hPa level for January 2010 in the NASA Goddard Earth Observing Model Version 5 (26). Values are calculated from the sensitivity of droplet number concentration to vertical velocity, temperature, aerosol modal number concentration, diameter, and chemical composition using the adjoint of the droplet parameterization and the input variances. Vertical velocity variation controls the droplet number concentration variability over continents and large fractions of the ocean with considerable influences from biogenic and anthropogenic emissions. Areas in white correspond to regions where stratus cloud fraction is low.