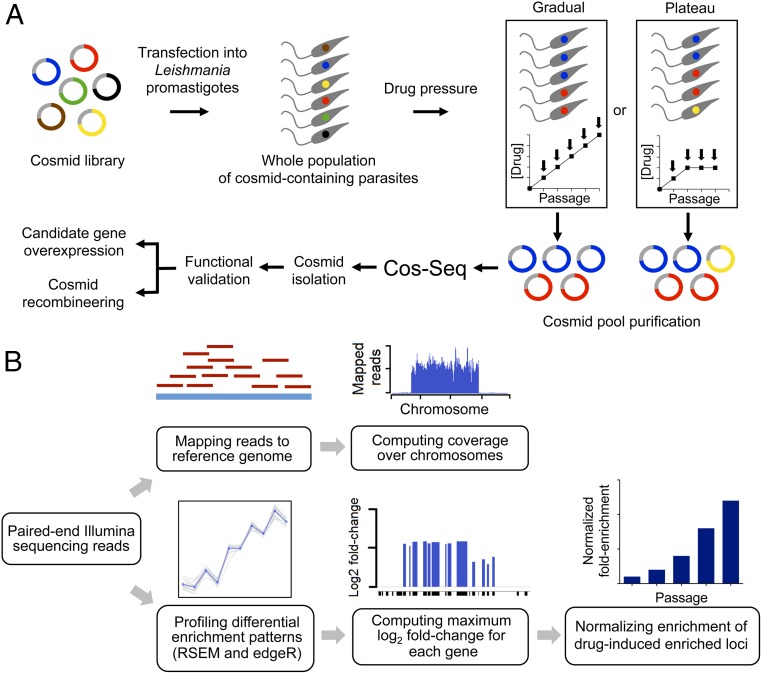
Fig. 1.
Overview of the Cos-Seq approach. (A) A WT L. infantum cosmid library cloned into the cLHYG vector (22, 23) is introduced into drug-susceptible L. infantum parasites. Pooled transfectants are submitted to incremental drug pressure starting at 1× EC50 and then increasing the drug concentration by twofold at each consecutive passage (from 1× EC50 to 16× EC50 depending on the drug; gradual selection strategy). Alternatively, a plateau selection scheme was used that allows parasites to adapt to a fixed drug concentration for two or three passages (plateau selection strategy). Cosmids are extracted from each selection step and purified for subsequent Illumina sequencing. The composition of cosmid pools at each drug/passage increment is determined from the NGS data, and cosmids of interest are isolated for functional validation. The relevant resistance genes are identified by gene overexpression studies and/or cosmid recombineering (29). (B) Sequencing reads are mapped to the reference genome, and gene coverage is inferred from the mapping data. Gene abundance and differential enrichment profiles are generated using RSEM (26) and edgeR (27), respectively. Genes are clustered according to their enrichment profiles. Genes located on the same cosmid are expected to have similar enrichment profiles. Gene abundance ratios are computed on a per-gene basis and normalized to the drug-free control.