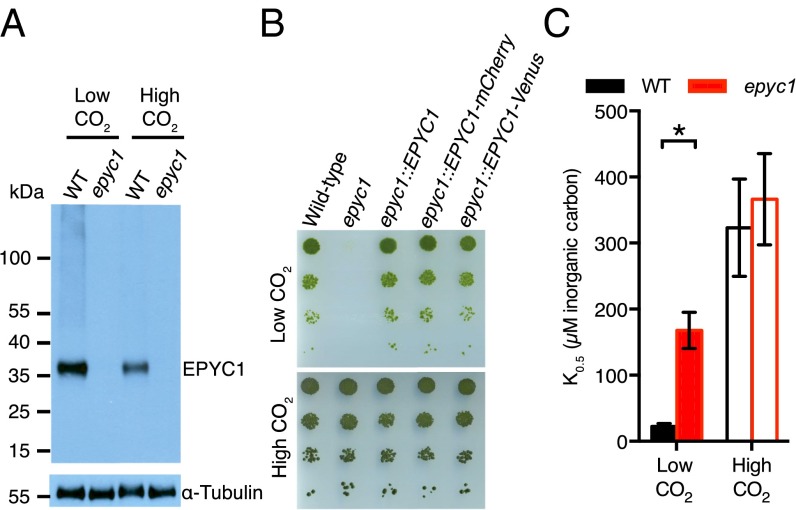
Fig. 2.
EPYC1 is an essential component of the carbon-concentrating mechanism. (A) EPYC1 protein levels in WT and epyc1 mutant cells grown at low and high CO2 were probed by Western blot analysis with anti-EPYC1 antibodies. Anti-tubulin is shown as a loading control. (B) Growth phenotypes of WT, epyc1, and three lines complemented with EPYC1. Serial 1:10 dilutions of WT, epyc1, epyc1::EPYC1, epyc1::EPYC1-mCherry, and epyc1::EPYC1-Venus lines were spotted on TP minimal medium and grown at low and high CO2 under 500 µmol photons m−2 s−1 illumination. (C) Inorganic carbon affinity of WT and epyc1 cells. Cells were pregrown at low and high CO2, and whole-cell inorganic carbon affinity was measured as the concentration of inorganic carbon at half-maximal O2 evolution. Data are a mean of five low-CO2 or three high-CO2 biological replicates. Error bars represent SEM. *P = 0.0055, Student’s t test.