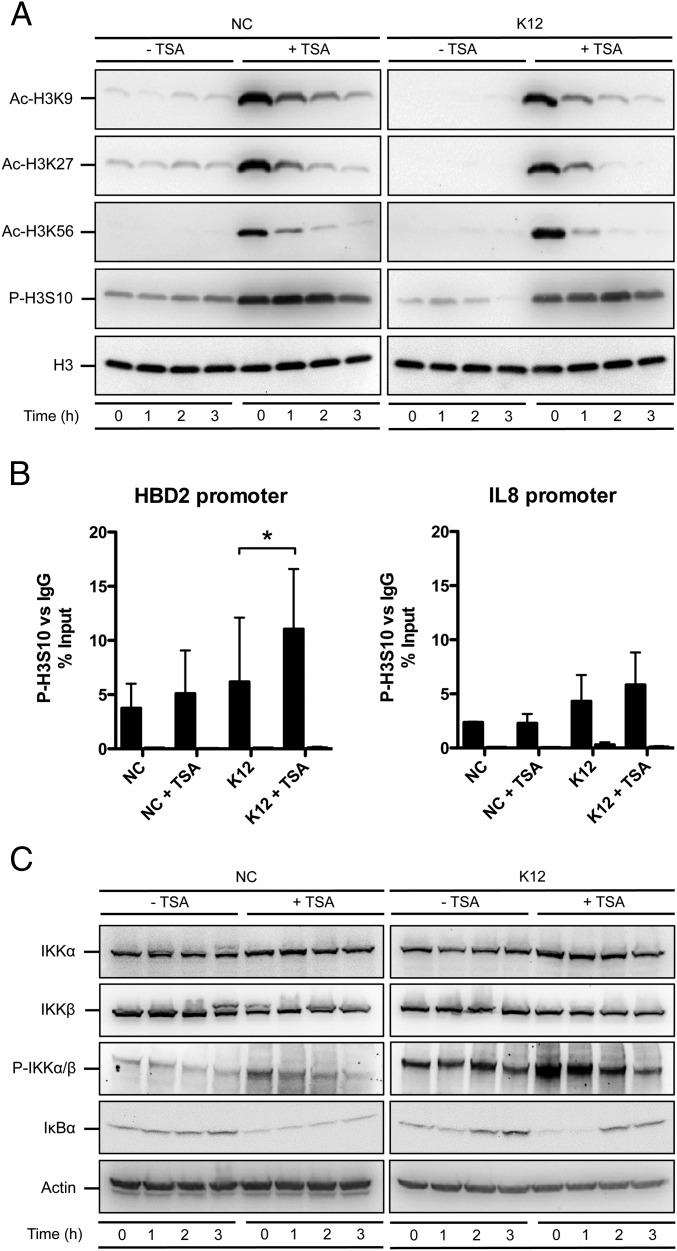
Fig. 2.
HDAC inhibition activates the IKK complex and induces phosphorylation of the histone H3 protein. (A) Immunoblot analysis of histone H3 acetylation on lysine K9, K27 and K56, and phosphorylation on serine S10, in cells pretreated or not for 16 h with 5 μM TSA, and then challenged or not with E. coli. After lysis of cells at the indicated time points, Western blots were performed using antibodies directed against histone posttranslational modification marks. NC, nonchallenged cells; K12, cells challenged with the E. coli K12 strain; “Ac” prefix, acetylation; “P” prefix, phosphorylation. (B) ChIP analysis of the phosphorylated H3S10 protein at the HBD2 and IL-8 promoters, in cells pretreated or not for 16 h with 5 μM TSA, and then challenged or not for 1 h with E. coli. Enrichment in chromatin was detected using anti–P-H3S10 antibody or rabbit IgG as control, and quantified by qRT-PCR using specific primers matching the HBD2 or IL-8 promoters. Values are presented as the percentage of signal relative to the input. NC, nonchallenged cells; NC+TSA, nonchallenged cells pretreated with 5 μM TSA; K12, cells challenged with the E. coli K12 strain; K12+TSA, cells pretreated with 5 μM TSA and challenged with the E. coli K12 strain. Black bars, signal detected using the P-H3S10 antibody; white bars, signal detected using the IgG control. *P < 0.05 evaluated by Mann–Whitney u test. (C) Immunoblot analysis of the IKKα and IKKβ proteins, the IKKα/β complex phosphorylation, and the IκBα protein, in cells pretreated or not for 16 h with 5 μM TSA, and then challenged or not with E. coli. After lysis of cells at the indicated time points, Western blots were performed using antibodies directed against proteins or posttranslational modification marks. NC, nonchallenged cells; K12, cells challenged with the E. coli K12 strain; “P” prefix, phosphorylation.