Figure 1.
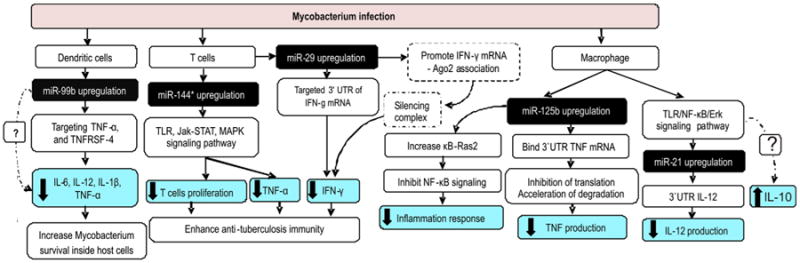
The roles of miRNAs in pathology tuberculosis infection. Several studies revealed evidence that Mycobacterium species infection in several cell types upregulated miR-99b, miR-144*, miR-29 and miR-125b. These miRNAs target several genes that are important in tuberculosis immunity. Upregulated of these miRNAs help Mycobacterial to survival inside host cells and enhance anti-tuberculosis immunity by inhibiting production of proinflammatory cytokines and inducing IL-10 through several mechanisms. Abbreviation: 3′UTR: 3′-untranslated region, Ago2: Argonaute 2, IFN-γ: Interferon-γ, IL-12: Interleukin 12, IL-1β: Interleukin 1β, IL-6: Interleukin 6, Jak-STAT: Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, NF-κB: nuclear factor κ beta, TLR: Toll-like receptor, TNFRSF-4: tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 4, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α.
