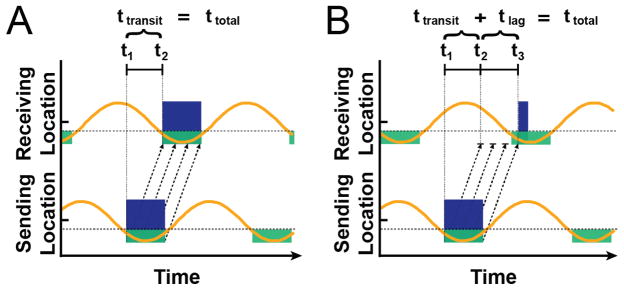
Figure 5.
Alpha oscillations may modulate the timing of communication between neuronal populations. As alpha amplitude (orange lines) decreases past a threshold voltage (dotted gray lines), neuronal populations may process and transmit information (i.e., permissive window, green boxes). When one population attempts to signal another, the time it takes for a series of spike volleys (black dotted arrows) to result in excitation of population activity (blue boxes) depends on the phase of the receiving population’s oscillatory activity. In A, the first spike volley immediately excites the receiving population. In B, most spike volleys do not arrive during a permissive window, delaying excitation.