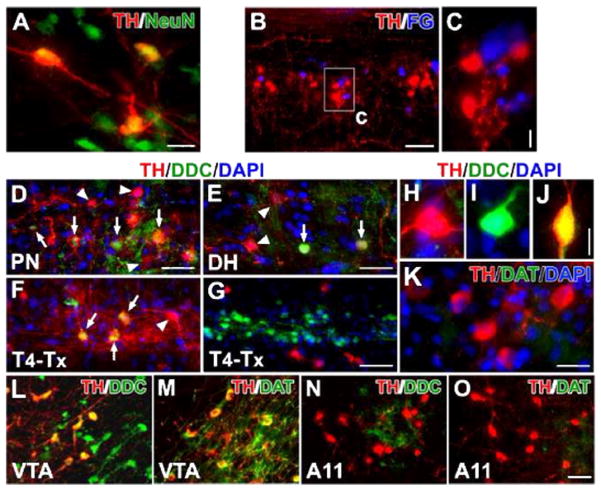
Fig. 3.
Lumbosacral TH+ cells are spinal interneurons and exhibit DA-ergic characteristics. A, In a coronal section of the lumbosacral spinal cord, TH+ cells co-express the mature neuronal marker NeuN. B, C, Parasympathetic preganglionic neurons (PPNs) were retrogradely labeled by i.p. injections of Fluorogold (FG). Though TH+ cells and FG-labeled cells are juxtaposed in the autonomic nuclei, no cells containing both TH and FG were detected. D–J, In both the parasympathetic nuclei (D) and superficial dorsal horn (E), some TH+ cells co-express DDC (arrows), suggesting the capacity for DA synthesis. The arrowhead highlights a TH+ cell that does not co-express DDC. Three weeks following T4–Tx, after the degeneration of descending catecholaminergic fibers, TH+/DDC+ cells (arrows) are identified more easily in the lateral autonomic region (F). Very few TH−/DDC+ cells are observed in the dorsal and medial gray matter whereas numerous TH−/DDC+ neurons are located in the layers around the central canal and many TH+ neurons reside in the neighboring regions (G). A representative TH+/DDC− (H), TH−/DDC+ (I), or TH+/DDC+ (J) neuron in the lumbosacral spinal cord. K, Dopamine transporter (DAT) is not detected in TH+ neurons. L–O, TH+ neurons in the VTA express strong signals of DDC (L) and DAT (M). However, the majority of TH+ neurons in the A11 nucleus do not contain or express very little DDC (N); A11 TH+ neurons do not express DAT (O). Images B–K are from longitudinal spinal cord sections and L–O are from sagittal brain sections. Scale bars: A, 20 μm; B, 100 μm; C, 10 μm; D, G, O, 50 μm; E, 32 μm; J, 12 μm; K, 25 μm.