Figure 1.
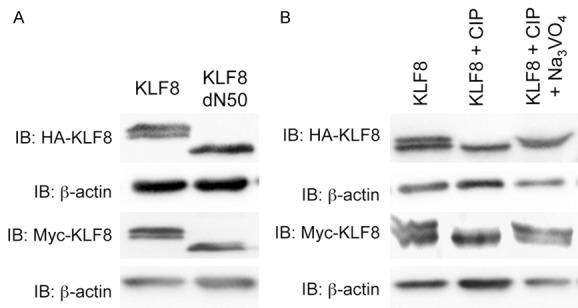
Mobility shift of KLF8 is due to phosphorylation in its N-terminal 50 amino acid residues. A. The N-terminal region of 50 residues is required for maintaining the doublet of KLF8 protein on SDS-PAGE gels. HA-KLF8, HA-KLF8-dN50, Myc-KLF8 or Myc-KLF8-dN50 was transfected into HEK293 cells. Whole cell lysates were collected after 48 hours and processed for western blotting with anti-HA (1:3000) or anti-Myc (1:2000) antibody with anti-β-actin as loading control. B. Treatment with alkaline phosphatase abolished the upper band of the KLF8 doublet. HA-KLF8 or Myc-KLF8 was oeverexpressed in HEK293 cells. Lysates prepared from the cells were treated with CIP without or with its inhibitor sodium orthovanadate (Na3VO4) as described in the Experimental Procedures and processed for western blotting as described above.
