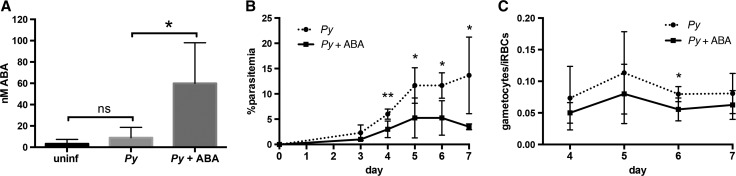
Figure 1.
Oral supplementation of abscisic acid (ABA) increased plasma ABA levels and decreased parasitemia and gametocytemia in mice. (A) Concentrations of ABA in plasma of uninfected CD1 mice and on day 7 post-Plasmodium yoelii infection with and without ABA treatment. Four to five mice were used per group. Data were analyzed using the Mann–Whitney test. (B) Daily percent parasitemia of control and ABA-supplemented mice infected with P. yoelii. (C) Gametocytemia, measured as the proportion of gametocytes in infected red blood cells (RBCs). Data for (B) and (C) are shown as means of four mice per group. Daily parasitemia and gametocytemia were analyzed by unpaired t test. * P ≤ 0.05, ** P ≤ 0.01.