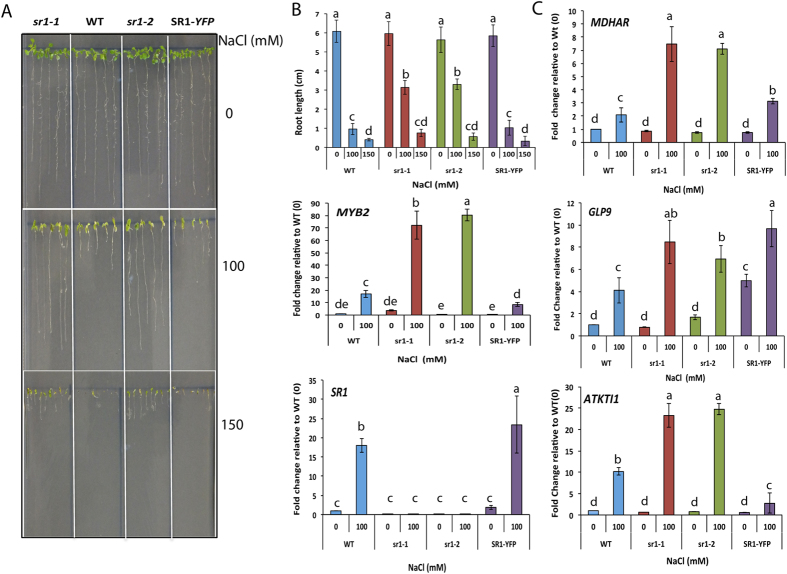
Figure 6. SR1 is a negative regulator of salt tolerance.
(A) Growth of seedlings of WT, sr1-1, sr1-2 and SR1-YFP on MS plates containing different concentrations of salt. Seeds were plated on ½ strength MS medium supplemented with 0, 100 and 150 mM of NaCl and were allowed to germinate and grow for two weeks. The photographs were taken after two weeks. (B) Top panel: root length was measured for each seedling for all four genotypes and plotted against the concentration of NaCl. Three biological replicates were used. Eight seedlings for each genotype per treatment for each biological replicate were included. Middle and Bottom panels: Expression levels of MYB2 and SR1 TFs under salt stress in different genotypes. Two-week-old seedlings grown on MS medium supplemented with 0 and 100 mM NaCl concentrations were used. A significant increase in the expression of these two TFs was observed. Salt-induced enhancement of MYB2 expression level was significantly higher in sr1-1 and sr1-2 lines. (C) SR1 regulates the expression of other salt-responsive genes. Expression levels of MDHAR, GLP9 and ATKTI1 in two-weeks-old seedlings exposed to 0 and 100 mM NaCl are determined by RT-qPCR. The expression levels of salt-responsive genes were normalized with ACTIN2. Fold change in expression level relative to WT controls (WT-0) is presented. WT-0 values were considered as 1. Student t-test was performed and significant differences (P < 0.05) among samples are labeled with different letters. The error bars represent SD.