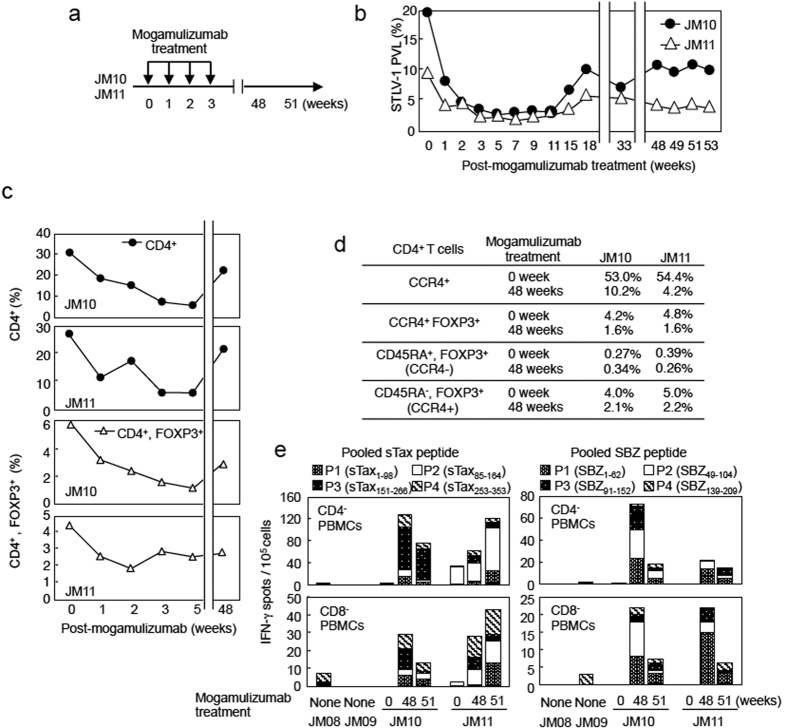
Figure 1. Mogamulizumab induces the activation of a virus-specific T-cell response in STLV-1-infected Japanese macaques.
(a) Scheme of mogamulizumab treatment in JM10 and JM11. (b) Changes in proviral load (PVL) in STLV-1-infected JM10 and JM11 after mogamulizumab treatment. PVL data before 18 weeks were reported previously17. (c) Changes in percent of PBMCs that are CD4+ or CD4+FOXP3+ after mogamulizumab treatment. (d) Proportion of CD4+ cells that are CCR4+, CCR4+FOXP3+, CD45RA+FOXP3+ or CD45RA−FOXP3+ at pre- and post- mogamulizumab treatment. Positive cells were gated based on each isotype control (>0.2%). (e) T-cell responses to sTax and SBZ before and after treatment with mogamulizumab. Monkey PBMCs were obtained before (0 weeks) and after (48 and 51 weeks) treatment and their response was measured by IFN-γ ELISPOT assay using pooled peptides of sTax or SBZ. Data from STLV-1-infected JM08/09 (before mogamulizumab treatment and vaccination) are presented as controls.