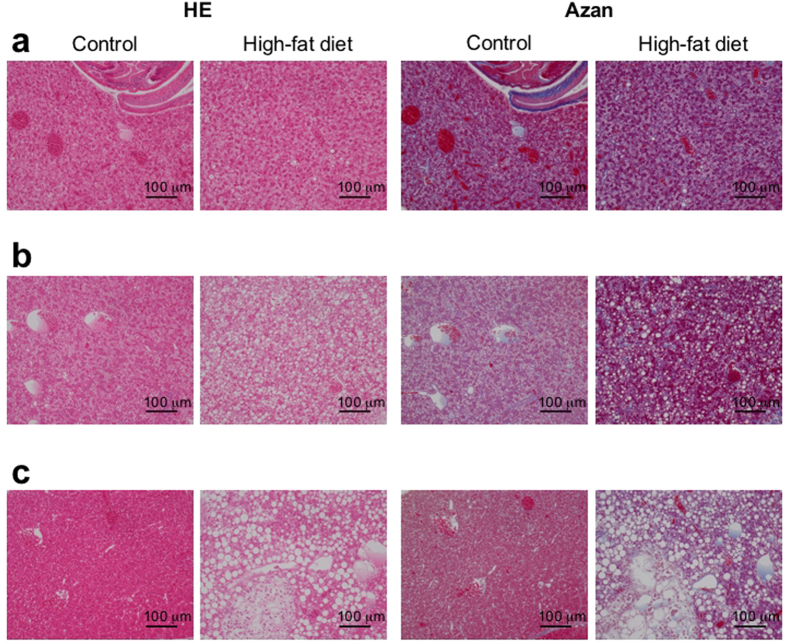
Figure 2. Feeding a high-fat diet induces hepatic steatosis in medaka.
(a) Histological analysis in medaka (Kyoto-cab strain) fed an HFD for 6 weeks (right sub-column) and in medaka (Kyoto-cab strain) maintained under control conditions for 6 weeks (left sub-column) using haematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining (left column) and azan staining (right column). Scale bars represent 100 μm. (b) Histological analysis in medaka (Kyoto-cab strain) of the 12 weeks HFD period (right sub-column) and in medaka (Kyoto-cab strain) maintained under control conditions for 12 weeks (left sub-column) using HE staining (left column) and azan staining (right column). The HFD group showed severe steatosis and hepatocellular ballooning. The azan staining indicated fibrosis in the HFD group. Scale bars represent 100 μm. (c) Histological analysis in medaka (Kyoto-cab strain) of the 16 weeks HFD period (right sub-column) and in medaka (Kyoto-cab strain) maintained under control conditions for 16 weeks (left sub-column) using HE staining (left column) and azan staining (right column). HE staining revealed an improvement of steatosis in the control group. The HFD group showed a heterogeneous distribution of larger lipid droplets and hepatocellular ballooning. Scale bars represent 100 μm.