Figure 9. A schematic diagram illustrating miR-185 and ATR function in radiation response.
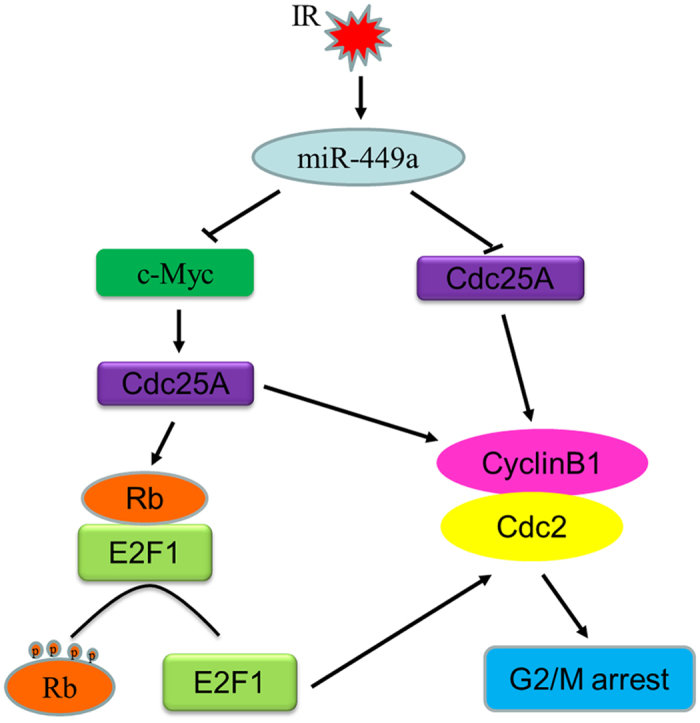
MiR-449a is induced in LNCaP cells following exposure to ionizing radiation. Elevated miR-449a represses c-Myc expression by by directly targeting the 3′-UTR of c-Myc mRNA. Cdc25A, as a mediatior of Myc function, is suppressed or degraded in response to DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation, resulting in dramatical inhibition of pRb phosphorylation and reduced E2F1 expression. Upon Rb phosphorylation, E2F proteins are released to activate downstream gene Cdc2. Cdc25A itself is a direct target of miR-449a and is capable of binding to cyclinB1 and activate Cdc2/cyclinB1 complexes. Consequently, miR-449a enhanced radiation-induced G2/M phase arrest and sensitizes cancer cells to ionizing radiation by downregulating c-Myc/Cdc25A pathway or directly repressing Cdc25A to modulate the Cdc2/cyclinB1 complexes.
