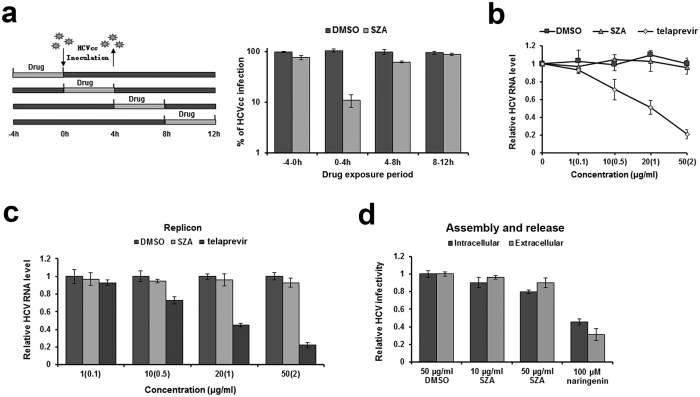
Figure 3. SZA has no inhibitory effect on viral replication, assembly and release.
(a) Huh7 cells were infected with HCVcc of JFH-1 (MOI = 1) and treated by 20 μg/ml of SZA for 4 h during indicated time periods as shown in the left panel. At 48 h post-infection, infected cells were performed IF. Results are plotted as % of HCVcc infection compared to DMSO treated group in parallel. (b) Antiviral activity of SZA on replication. JFH-1 RNA was electroporated into Huh7 cells. At 4 h after electroporation, the cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of SZA for 4 h at 37 oC. Concentrations of telaprevir are shown in brackets of the figure. Results are shown as relative HCV RNA level compared to untreated group. (c) BB7 replicon cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of SZA or telaprevir for 4 h. Viral RNA levels were determined by qPCR 48 h after treatment. Concentrations of telaprevir are in brackets of the figure. Results are plotted as relative HCV RNA level compared to DMSO treated group. (d) Antiviral activity of SZA on assembly and release. Huh7 cells were electroporated with JFH-1 RNA of HCV, followed by 4 h treatment of the indicated concentrations of SZA. At 48 h after electroporation, cells were subjected to three cycles of freeze and thaw to test the intracellular viral infectivity; supernatants of the electroporated cells were collected for the detection of extracellular viral infectivity. 100 μM naringenin was introduced as a positive control. Results are shown as relative HCV infectivity compared to DMSO treated group. Data shown as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.