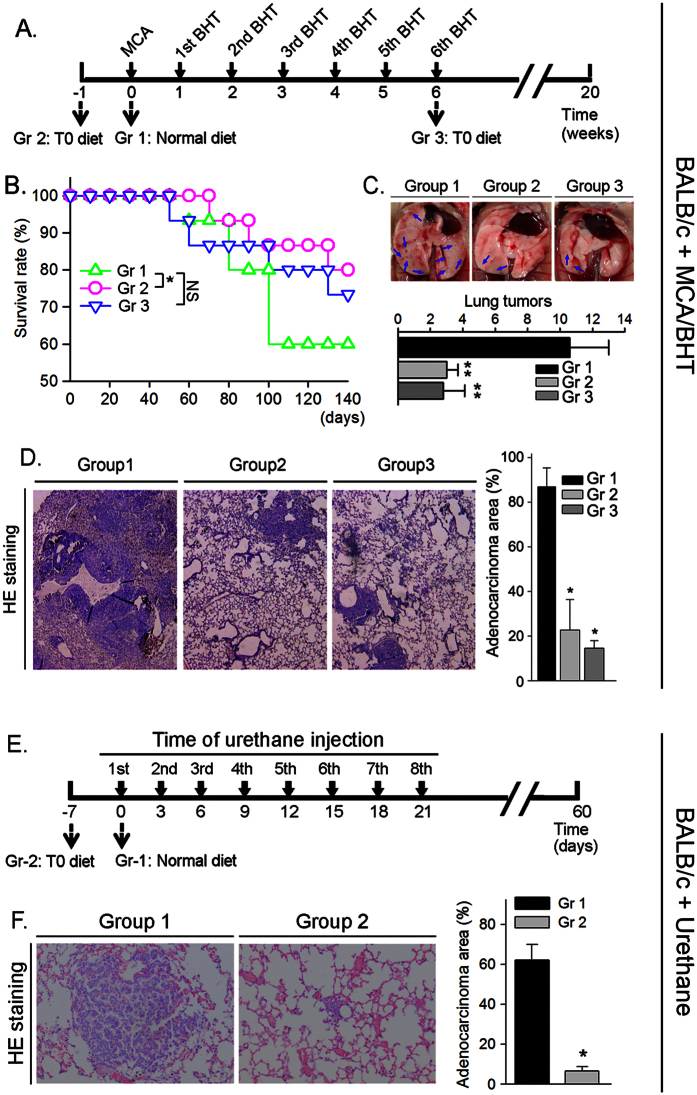
Figure 2. T0901317 inhibits formation of carcinogen-induced lung tumors in BALB/c wild type mice.
(A–D) BALB/c mice were divided into 3 groups (15 mice/group) and received the scheduled MCA/BHT injections. (A) the animals also received the following treatment: mice in Group 1 (Gr 1) were fed normal chow; mice in Group 2 (Gr 2) and Group 3 (Gr 3) were fed normal chow containing T0901317 (5 mpk) one week before and 6 weeks after MCA injection, respectively; (B) the death of MCA/BHT-injected mice in each group was daily checked and the survival rate was plotted vs. time after MCA injection. *P < 0.05, NS: not significant difference; (C) representative photographs of lungs from each group after 20 weeks of MCA injection (top panel). The blue arrows indicate the visible tumors on the surface of the lung. The lung tumors formed in each mouse were counted and the mean of tumor number in each group was plotted (low panel, n = 5; **P < 0.01 vs. Group 1); (D) lung sections from each group were prepared and conducted HE stained (left panel); the area filled with tumors was determined as % of whole section (right panel). *P < 0.05 vs. group 1 (n = 5); (E) BALB/c mice were divided into 2 groups (15 mice/group) and fed normal chow or normal chow containing T0901317 (5 mpk). One week later, all the mice were i.p. injected with urethane (1 g/kg bodyweight) once every 3 days for 8 times; (F) at the end of the experiment, the urethane-injected mouse lung sections were prepared following by HE staining and determination of tumor area (% of whole section). *P < 0.05 vs. Group 1 (n = 15).