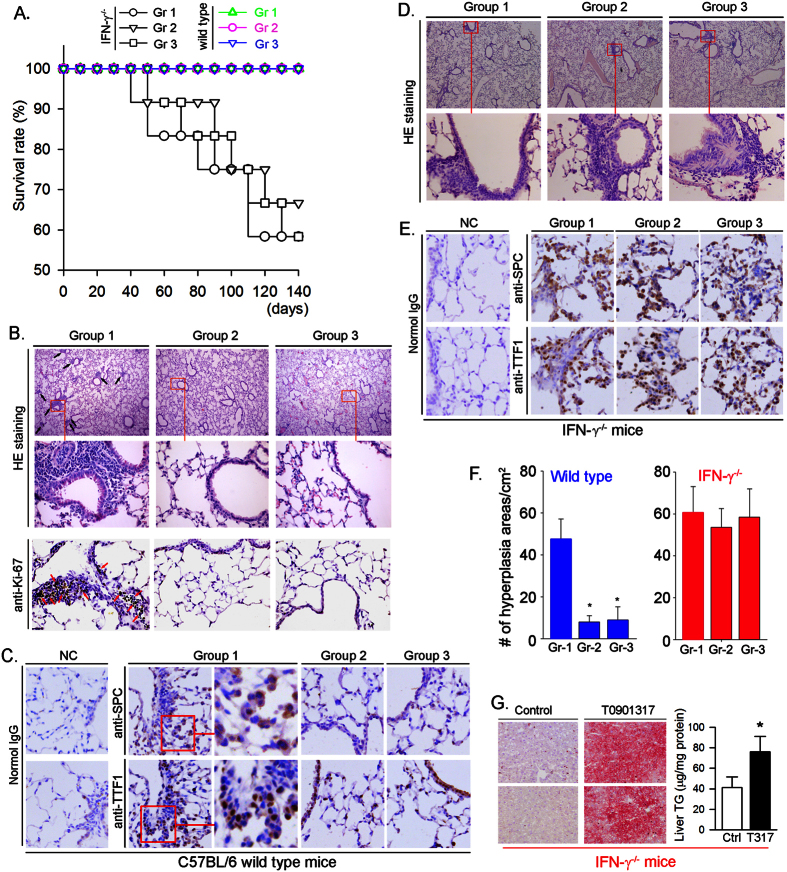
Figure 3. T0901317 inhibits development of atypical hyperplasia and inflammation in C57BL/6 wild type mice, but not IFN-γ−/− mice.
C57BL/6 wild type mice or IFN-γ−/− (C57BL/6 background) mice were randomly divided into 3 groups (C57BL/6 wild type mice: 15 mice/group; IFN-γ−/− mice: 12 mice/group) and received the same treatment as indicated in Fig. 2A: Group 1 (Gr 1), fed normal chow; Group 2 (Gr 2), fed normal chow containing T0901317 (5 mpk) from one week before MCA injection; and Group 3 (Gr 3), fed normal chow containing T0901317 (5 mpk) from the 6th BHT (or 6 weeks after MCA) injection. (A) the death of mice in either C57BL/6 mice or IFN-γ−/− mice was daily checked after MCA injection. No significant difference was determined among groups either of C57BL/6 mice or IFN-γ−/− mice. At the end of experiment, the lung sections were prepared and conducted HE staining: B (top panel), C57BL/6 mice; (D) surviving IFN-γ−/− mice. Expression of Ki-67 ((B) low panel), SPC ((C) up panel) and TTF1 ((C) low panel) in lung sections of C57BL/6 mice were determined by immunohistochemical staining with the corresponding primary antibody. The enlarged images (right panel of Group 1, (C)) demonstrate that SPC and TTF1 localize in cellular cytosol and nuclei, respectively; (E) expression of SPC and TTF1 in lung sections of IFN-γ−/− mice was determined by immunohistochemical staining; (F) areas with hyperplasia/inflammation and size >200 μm2 were counted from more than 3 lung sections in each of C57BL/6 wild type mice and IFN-γ−/− mice. *P < 0.05 vs. Gr 1; (G) IFN-γ−/− mice were divided into two groups (5 mice/group) and fed normal chow (Control, Ctrl) or normal chow containing T0901317 at 5 mpk (T0901317, T317), respectively, for two weeks. Lipid content in the liver was determined by Oil Red O staining (left panel) and TG quantitative assay (right panel), *P < 0.05 (n = 5).