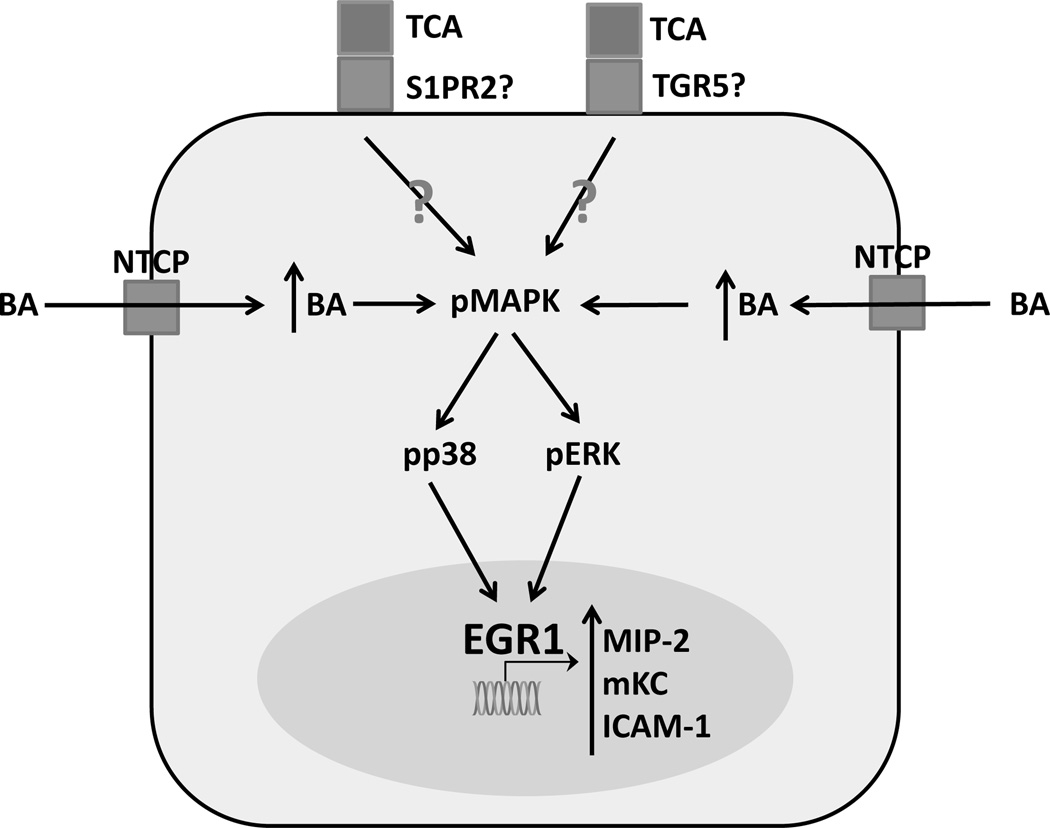
Figure 1.
Bile acid signaling in murine hepatocytes. Cultured hepatocytes exposed to conjugated bile acids such as taurocholic acid active a signaling pathway that results in dramatic increases in expression of pro-inflammatory mediators. TCA – taurocholic acid, S1PR2 – sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor 2, GPBAR-1 – G-protein bile acid coupled receptor-1, BA – bile acid, NTCP – sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide, pMAPK – phosphorylated mitogen activated protein kinase, pp38 – phosphorylated protein-38, pERK – phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinase, Egr1 – early growth response factor 1, MIP-2 – macrophage inflammatory protein 2, mKC – mouse keratinocyte factor, ICAM-1 – intercellular adhesion molecule-1, OATP – organic anion transporting polypeptide, TGR5/GPBAR-1 – G-protein coupled bile acid receptor