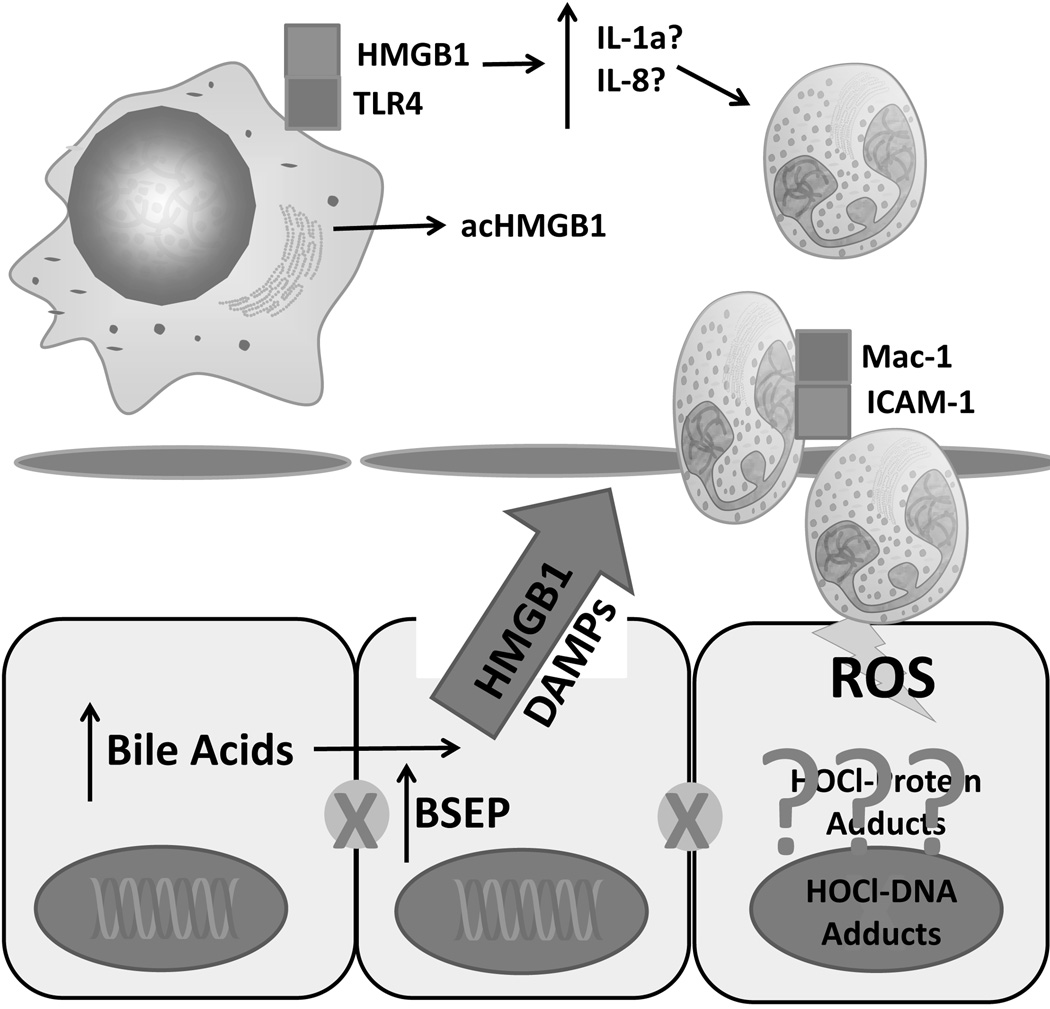
Figure 3.
Model for bile acid-induced necrosis in man. Increases in cellular bile acid levels leads directly to cell death when exposed to biliary bile acid concentrations. This results in release of damage associated molecular patterns such as HMGB1 and potentially other DAMPs. Current research is attempting to determine if the subsequent recruitment of neutrophils is mediated by specific cytokines, and if neutrophils worsen injury after cholestasis. BA – bile acid, HMGB1 – high mobility group box-1, DAMP – damage associated molecular pattern, acHMGB1 – acetylated HMGB1, TLR-4, toll-like receptor 4, IL-1α – interleukin 1α, IL-8 - interleukin-8, ROS – reactive oxygen species, HOCl – hypochlorous acid, Mac-1- macrophage 1 antigen (CD11b/CD18), ICAM-1 – intercellular adhesion molecule 1