Figure 2. TBK1 Molecular Pathways.
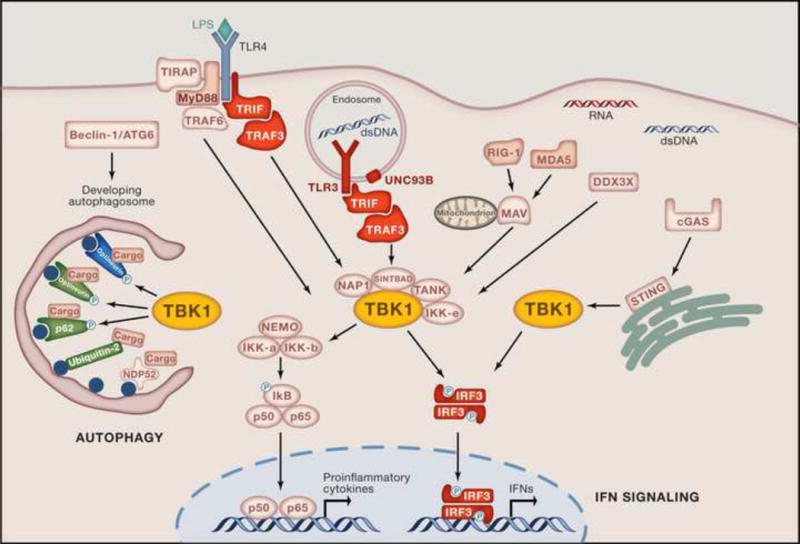
TBK1 and IKKɛ function as the non-canonical IkB kinases downstream of TLRs, RLRs, DDX3X, and DNA receptors leading to the activation of the transcription factors NF-kB (p65/p50) and IRFs (IRF3), resulting in the production of proinflammatory cytokines and antiviral IFNs. TLR3 recognizes dsRNA initiating the recruitment of adaptors such as TRIF and TRAF3 (TNF receptor-associated factor 3), which then activate TBK1 found in complex with its interacting proteins NAP1 (NF-kB-activating kinase-associated protein-1), SINTBAD (similar to NAP1 TBK1 adaptor) and TANK. LPS recognition by TLR4 can also recruit TRIF and subsequently TRAF3, mediating TBK1 activation. Activated TBK1 can then phosphorylate IRF3, leading to its homodimerization and subsequent translocation into the nucleus where it induces the production of IFNs. Cytosolic RLRs and DDX3X, as well as DNA sensor cGAS signal via TBK1 following recognition of their ligands viral 5′-ppp RNA and DNA, respectively. RLRs typically signal via the adaptor MAVS (mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; also known as IPS-1, CARDIF or VISA), which activates TBK1. cGAS detects dsDNA and stimulates STING (stimulator of interferon genes) to bind and activate TBK1 directly. TBK1 is also involved in autophagy where it directly phosphorylates the autophagy receptors optineurin and p62, which target cargo to the autophagosome. Ubiquilin-2 can also target ubiquitinated cargo to autophagosomes [113]. Target cargo may be comprising pathogen or ubiquitinated protein aggregates. Proteins whose genes have been reported to predispose to diseases are indicated in red, HSE; green, ALS or ALS-FTD; blue, NTG. Yellow denotes TBK1, where all pathways converge.
