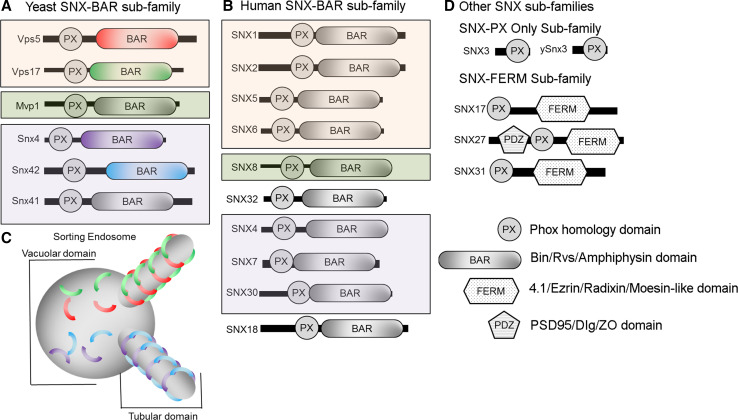
Fig. 2.
Key features of sorting nexins that mediate export from the endosome. All sorting nexins contain an evolutionarily conserved Phox-homology (PX) domain that recognizes phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate. a, b Members of the SNX-BAR sub-family of sorting nexins also contain a Bin-Amphiphysin-Rvs (BAR) dimerization domain that displays a curved surface and oligomerizes to coat the membrane of an endosome-derived transport carrier. Subsets of SNX-BARs (colored boxes) have been shown to homo- or heterodimerize. c Model of tubular ETC formation by SNX-BARs. SNX-BAR protomers coat both the vacuolar and tubular domains of the endosome and oligomerize to coat the tubular ETCs. Restricted oligomerization of SNX-BAR protomers, and dependence on other factors such as retromer, define distinct export pathways. d Other evolutionarily conserved SNX proteins implicated in endosome export. Members of the PX-only subfamily are comprised of a single PX domain. So far, SNX3 (and its yeast homolog, ySnx3) are the only members of this sub-family to be implicated in cargo export. Members of the SNX-FERM sub-family contain a C-terminal FERM (band4.1/ezrin/radixin/moesin) domain, which is a protein interaction module that is used for cargo recognition