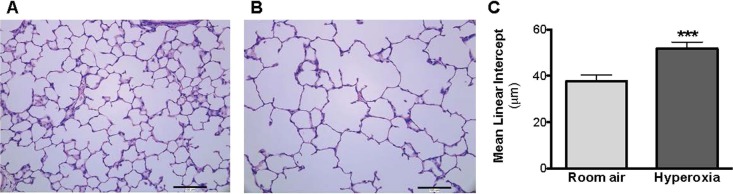
Fig. 1.
Hematoxylin and eosin-stained lung sections of P28 old rats exposed to room air (‘control’ group) or hyperoxia (‘BPD’ group) from P4 to P14. (A,B) Newborn rats were housed in 95% O2 from P4 to P14 and studied in comparison with control rats raised in room air. The exposure of rat pups to hyperoxia (B) during the alveolar stage of lung development results in arrested alveolar growth characterized by larger and fewer alveolar structures compared to (A) room air rat pups, as shown in hematoxylin and eosin-stained representative lung slides. (C) The mean linear intercept was measured to quantify alveolar structures. Data represented as mean±s.d.; ***P<0.001, comparison versus room air control group.