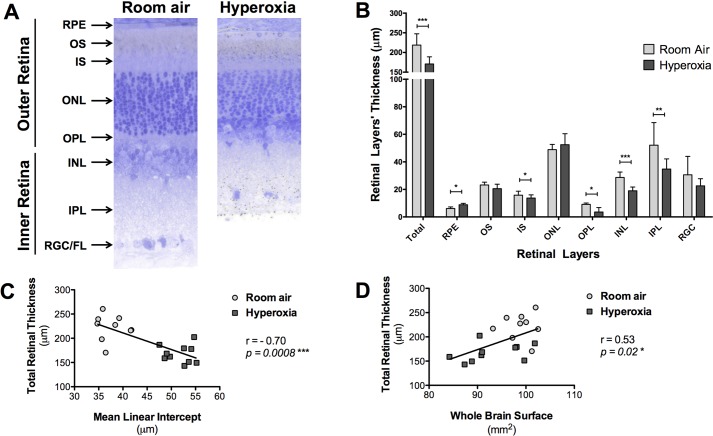
Fig. 4.
Toluidine Blue-stained retinal cross sections from the eyes of P28 old rats exposed to room air (‘control’ group) or hyperoxia (‘BPD’ group) from P4 to P14. (A) Representative retinal cross sections, images were taken at approximately 1000 µm from the optic nerve head in the inferior retina. (B) Thickness of the retinal layers measured at 1000 µm from the optic nerve head. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; OS, outer segment; IS, inner segment; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; RGC/FL, retinal ganglion cell/fiber layer. Data represented as mean±s.d.; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 in the hyperoxia-exposed rat pups compared to the room air-exposed rat pups. (C) Comparison between the average total retinal thickness measured (reflecting retinal structure) and the mean linear intercept (reflecting lung alveolar structure), showing a negative correlation between both structures (r=−0.58, P=0.009). (D) Comparison between the average total retinal thickness measured (reflecting retinal structure) and the whole-brain surface measured on the posterior sections (reflecting brain structure), showing a positive correlation between both structures (r=0.55, P=0.01).