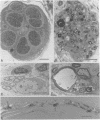
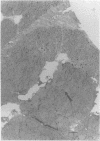
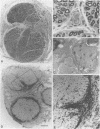
Abstract
Eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome (EMS) is a newly described syndrome associated with use of L-tryptophan. A neuropathy with features of axonal degeneration has also been described in conjunction with EMS. Demyelinating polyneuropathy is not a well recognised association of the syndrome. The two patients with EMS reported presented with profound weakness and sensory loss and were found to have clinical, electrophysiological and pathological evidence of a chronic demyelinating polyneuropathy. The concurrence of this neuropathy with EMS, as well as several other features of their illness, is suggestive of an immune mediated mechanism in the pathophysiology of EMS.
Full text
PDF

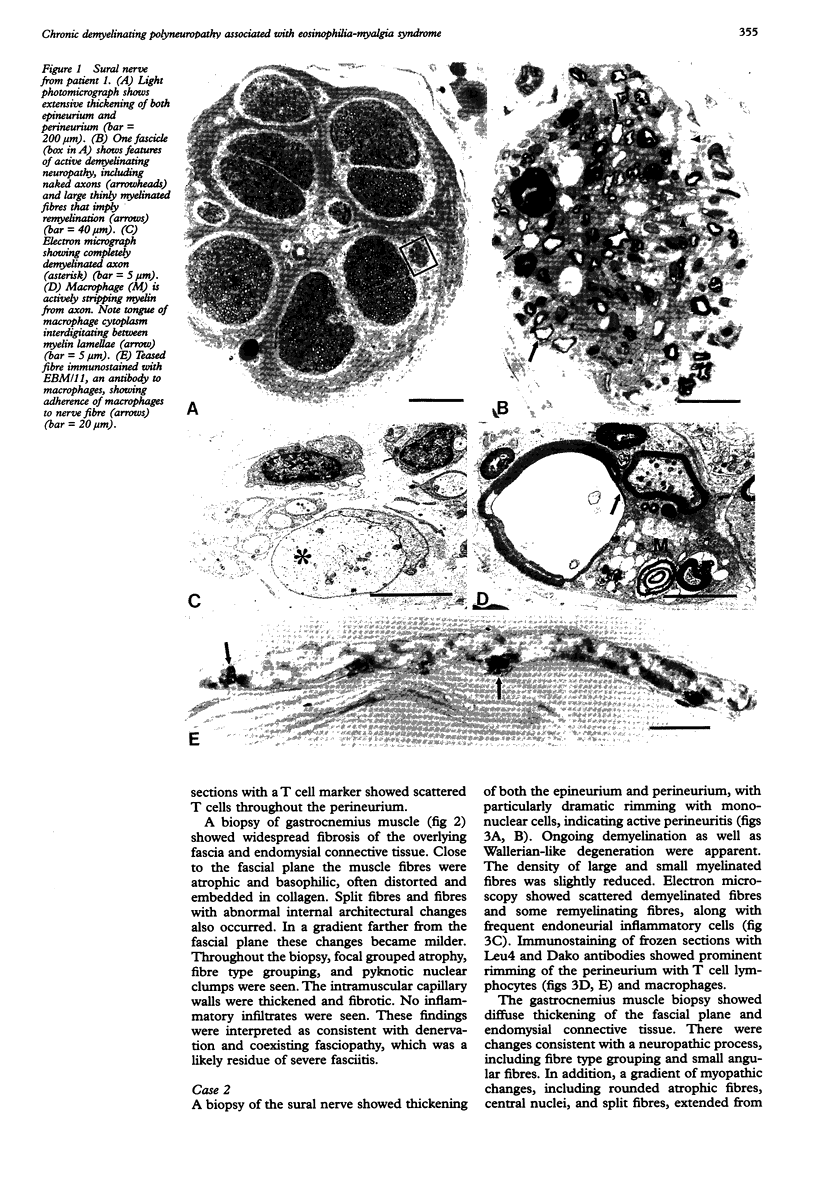

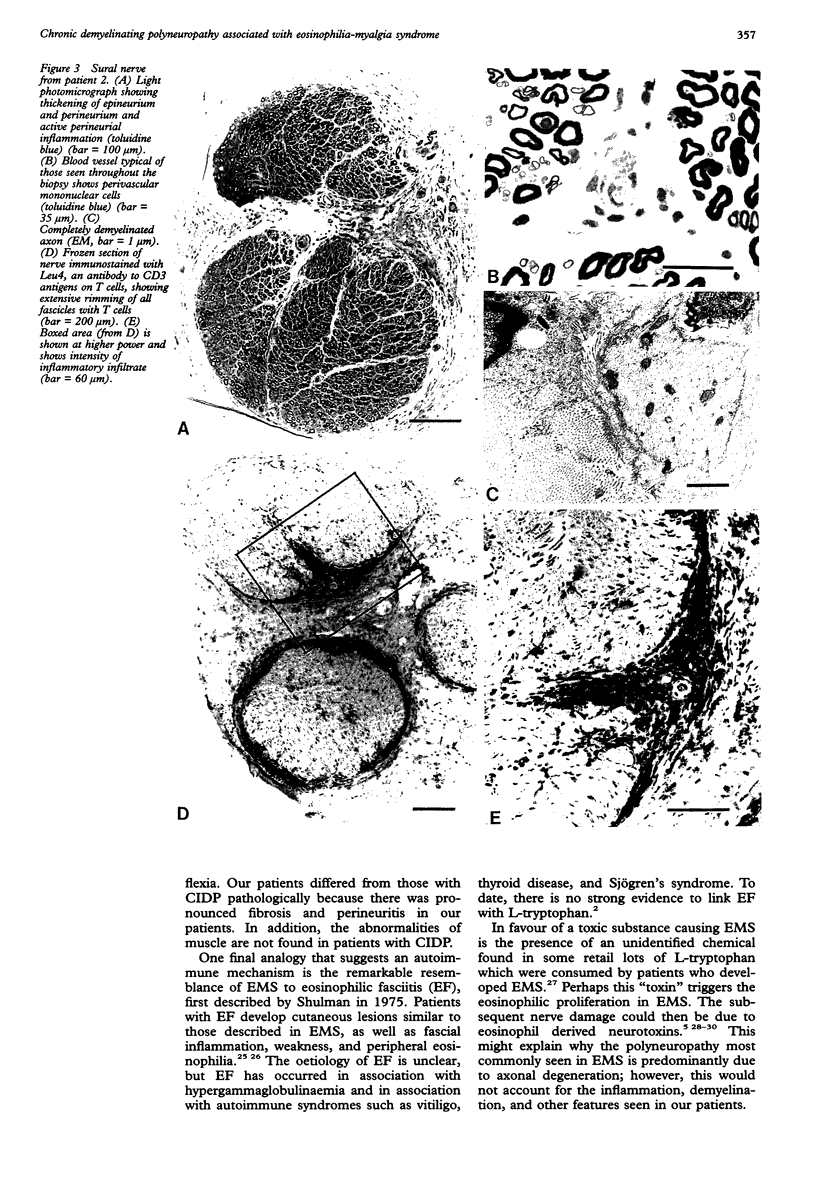

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arsura E. L., Bick A., Brunner N. G., Namba T., Grob D. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in the management of myasthenia gravis. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Jul;146(7):1365–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belongia E. A., Hedberg C. W., Gleich G. J., White K. E., Mayeno A. N., Loegering D. A., Dunnette S. L., Pirie P. L., MacDonald K. L., Osterholm M. T. An investigation of the cause of the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome associated with tryptophan use. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 9;323(6):357–365. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008093230601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. F., Feasby T. E. Conduction block and denervation in Guillain-Barré polyneuropathy. Brain. 1984 Mar;107(Pt 1):219–239. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.1.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Sumi S. M., Klebanoff S. J. Neurotoxicity of human eosinophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1443–1447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furusho K., Kamiya T., Nakano H., Kiyosawa N., Shinomiya K., Hayashidera T., Tamura T., Hirose O., Manabe Y., Yokoyama T. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for Kawasaki disease. Lancet. 1984 Nov 10;2(8411):1055–1058. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdos P., Outin H., Elkharrat D., Brunel D., de Rohan-Chabot P., Raphael J. C., Goulon M., Goulon-Goeau C., Morel E. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1984 Feb 18;1(8373):406–407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan J. S., Daniels T. E., Talal N., Sylvester R. A. The histopathology of Sjögren's syndrome in labial salivary gland biopsies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1974 Feb;37(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(74)90417-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Heininger K., Schäfer B., Fierz W., Toyka K. V. Immune mechanisms in inflammatory polyneuropathy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;540:122–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb27058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiman-Patterson T. D., Bird S. J., Parry G. J., Varga J., Shy M. E., Culligan N. W., Edelsohn L., Tatarian G. T., Heyes M. P., Garcia C. A. Peripheral neuropathy associated with eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1990 Oct;28(4):522–528. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzman P. A., Blevins W. L., Mayer J., Greenfield B., Ting M., Gleich G. J. Association of the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome with the ingestion of tryptophan. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 29;322(13):869–873. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medsger T. A., Jr Tryptophan-induced eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 29;322(13):926–928. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. M., Harley J. B., Fauci A. S. Neurologic dysfunction in the idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Jan;102(1):109–114. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestronk A., Adams R. N., Clawson L., Cornblath D., Kuncl R. W., Griffin D., Drachman D. B. Serum antibodies to GM1 ganglioside in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology. 1988 Sep;38(9):1457–1461. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.9.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestronk A., Cornblath D. R., Ilyas A. A., Baba H., Quarles R. H., Griffin J. W., Alderson K., Adams R. N. A treatable multifocal motor neuropathy with antibodies to GM1 ganglioside. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jul;24(1):73–78. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Research criteria for diagnosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). Report from an Ad Hoc Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology AIDS Task Force. Neurology. 1991 May;41(5):617–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahenk Z., Mendell J. R., Rossio J. L., Hurtubise P. Polyradiculoneuropathy accompanying procainamide-induced lupus erythematosus: evidence for drug-induced enhanced sensitization to peripheral nerve myelin. Ann Neurol. 1977 Apr;1(4):378–384. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwa J. F., Feldman E. L., Blaivas M. Mononeuropathy multiplex in tryptophan-associated eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. Neurology. 1990 Oct;40(10):1632–1633. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.10.1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman L. E. Diffuse fasciitis with eosinophilia: a new syndrome? Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1975;88:70–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. M., Heyes M. P., Maize J. C., Quearry B., Vionnet-Fuasset M., Sternberg E. M. Scleroderma, fasciitis, and eosinophilia associated with the ingestion of tryptophan. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 29;322(13):874–881. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Dyck P. J. Peripheral neuropathy in the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome associated with L-tryptophan ingestion. Neurology. 1990 Jul;40(7):1035–1040. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.7.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll G., Griffin J. W., Li C. Y., Trapp B. D. Wallerian degeneration in the peripheral nervous system: participation of both Schwann cells and macrophages in myelin degradation. J Neurocytol. 1989 Oct;18(5):671–683. doi: 10.1007/BF01187086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunohara N., Furukawa S., Nishio T., Mukoyama M., Satoyoshi E. Neurotoxicity of human eosinophils towards peripheral nerves. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Aug;92(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treatment of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 9;323(6):417–418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008093230613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treatment of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 9;323(6):417–418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008093230613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyor W. R., Stoll G., Griffin D. E. The characterization of Ia expression during Sindbis virus encephalitis in normal and athymic nude mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1990 Jan;49(1):21–30. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199001000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Doorn P. A., Brand A., Strengers P. F., Meulstee J., Vermeulen M. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Neurology. 1990 Feb;40(2):209–212. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]