Fig. 7.
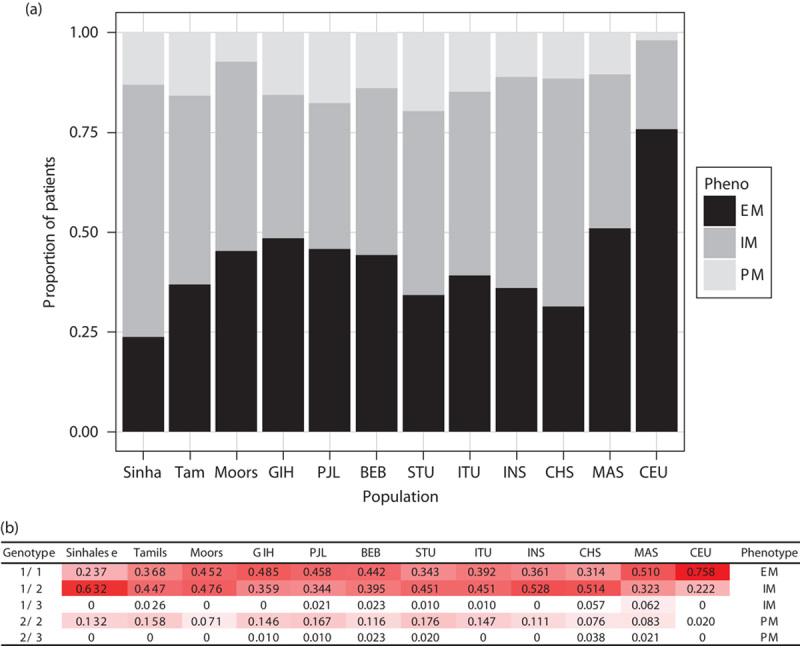
CYP2C19 phenotypes and genotype frequencies in the different populations. Predicted phenotype in terms of enzymatic activity of CYP2C19 (a) based on combinations of CYP2C19*2 and *3 variants (b). (a) Extensive metabolizers (EM) have normal platelet inhibition with clopidogrel, whereas intermediate metabolizers (IM) and poor metabolizers (PM) have reduced platelet inhibition. Alternative antiplatelets such as prasugrel or ticagrelor are recommended for patients who are IM or PM 31. Thus the black bars (EM) represent the proportion of patients who are expected to have good response to clopidogrel. (b) *Frequencies of genotype combinations for Sinhalese, Sri Lankan Tamils, and Moors were obtained from 118 participants (of 125 with DNA available) with successful TaqMan genotyping of CYP2C19*2 (rs4244285), those for MAS and INS were obtained from sequencing of Singapore Malays and Indians, respectively 23,32, and that for CHS was obtained from 1000 Genomes project (Southern Han Chinese). †Phenotypes were defined according to the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for clopidogrel. The intensity of red highlighting of genotype combination frequencies corresponds to their magnitude across the range observed [i.e. 0 (white)–0.758 (red)]. BEB, Bengali from Bangladesh; CEU, Utah residents with Northern and Western European ancestry; CHS, Chinese in Singapore; GIH, Gujarati Indians from Houston, Texas; INS, Indians in Singapore; ITU, Indian Telugu from the UK; MAS, Malays in Singapore; PJL, Punjabi from Lahore, Pakistan; STU, SL Tamils from the UK.
