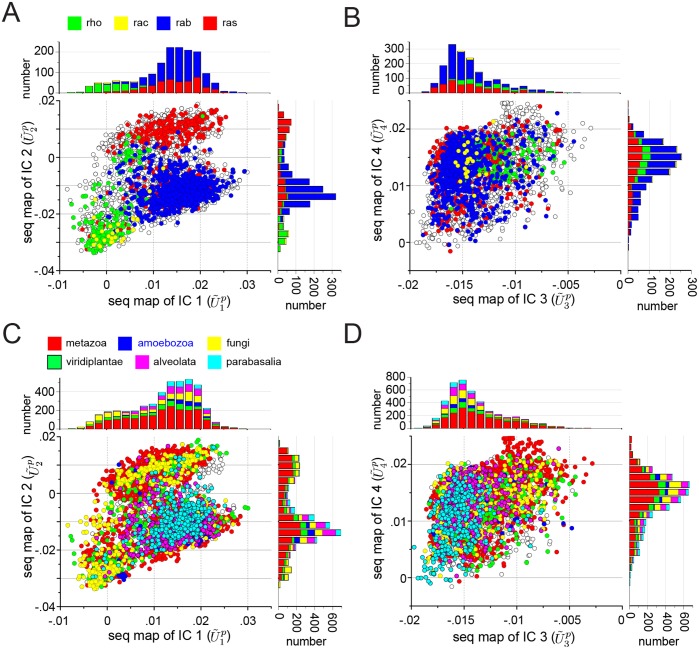
Fig 7. IC-based sequence divergences in the G protein family.
The panels show scatterplots of sequences in the G protein alignment along dimensions () that correspond to sequence variation in positions contributing to each of the four ICs of the SCA coevolution matrix. The mapping between positional coevolution to sequence relationships is achieved using the reduced alignment matrix x, as per Eqs (14) and (15). Sequences are colored either by annotated functional sub-type of G protein (A-B) or by taxonomic origin (C-D), and the stacked histograms show the distributions of these classifications for each dimension. The data show that ICs 1 and 2 (A) correspond to distinct sequence divergences of functional subtypes of G protein; for example, IC1 separates the Rho proteins (green) along , and IC2 separates the Rho proteins (green) and a subset of Ras proteins (red) along . In contrast, IC3 and IC4 are homogenous with regard to G protein subtype (B), and all ICs are essentially homogeneous with regard to phylogenetic divergence (C-D). These data suggest that IC3 and IC4 are nearly homogeneous features of the G protein family, while IC1 and IC2 are differentially selected for more specialized properties of G protein subtypes.