Figure 5. CagA-mediated DNMT1 upregulation is dependent on constitutive AKT phosphorylation and subsequent activated NFκB which combines to DNMT1 promoter.
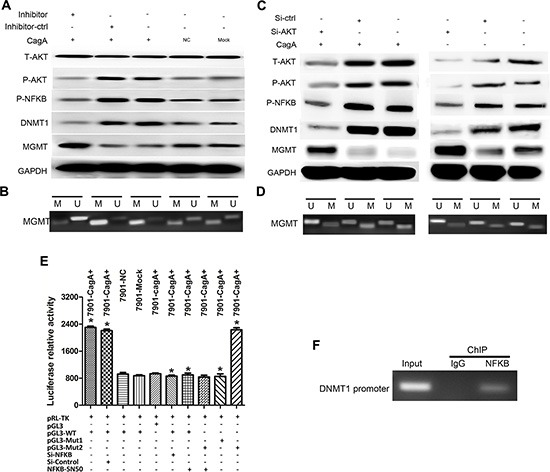
(A and C) WB analysis of related signal proteins in different groups after treated with AKT inhibitor (MK-2206 2HC) or AKT siRNAs. MGMT reduction in CagA+ SGC-7901 is reversed by AKT inhibitor or AKT siRNAs, On the other hand, T-AKT, P-PDK1/P-AKT/P-NFκB and DNMT1 expression significantly decrease in CagA+ cells compared with control cells. (B and D) MSP analysis of MGMT methylation in CagA+ SGC-7901 or EV-SGC-7901 after AKT inhibiton. MGMT hypermethylation is also markedly reversed in CagA+ SGC-7901 by AKT inhibitor or AKT siRNAs compared with control cells. (E) Reporter plasmids of DNMT1 (pGL3-DNMT1) are generated by ligating DNMT1 promoter region into the pGL3-basic vector. CagA transfection significantly increases luciferase activity, which is significantly reduced by NFκB inhibition. (F) DNMT1 promoter region and NFκB interaction is validated by the ChIP. Data shows that DNMT1 DNA is detectable in the ChIP sample of CagA+ SGC-7901 using an antibody against NFκB1 p50, suggesting that NFκB1 p50 binds to DNMT1 promoter. These data suggest that CagA increased DNMT1 expression may depend on NFκB activation. Results are expressed as relative expression compared with control cells (*p < 0.05). Each value is the mean ± SD of three experiments.
