Figure 2. In vivo anti-tumor effect of Rh2E2 on AOM/DSS-induced colon carcinogenesis and LLC-1 xenograft mouse model.
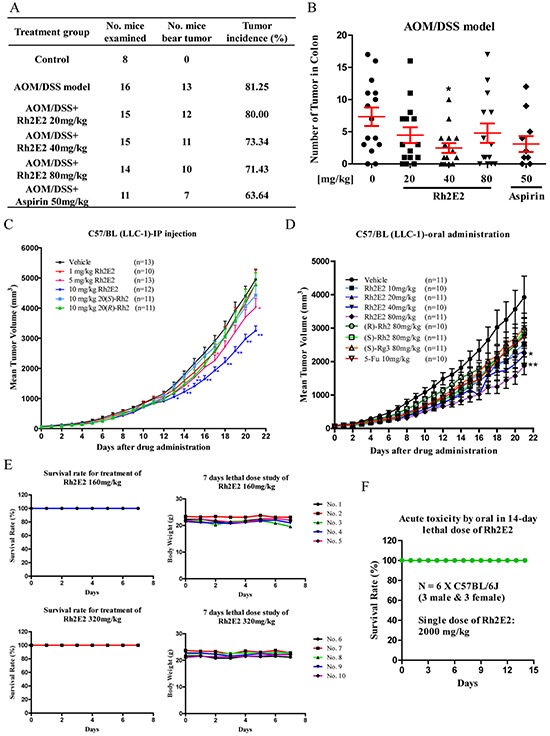
A. Effect of Rh2E2 on tumor incidence in AOM/DSS CRC model. Rh2E2 (20, 40 and 80 mg/kg/day) or positive control drug aspirin (50 mg/kg/day) dissolved in PEG400: Ethanol: water = 6:1:3 (v/v/v) was given to the mice by oral gavage administration for 11 weeks. The tumor incidence (%) of each group was calculated from the number of mice with developed colon cancer over the total number of mice examined. B. Effect of Rh2E2 on the number of tumors found in mouse colon. At necropsy, the mice colon were dissected longitudinally and the number of tumors were counted together with the volume of tumor in length (mm) × width (mm) × height (mm) measured by caliper. Data were presented as mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, versus AOM/DSS vehicle group. C. In vivo tumor suppression effect of Rh2E2 on LLC-1 xenograft via intraperitoneal (IP) injection. D. In vivo suppressive effect on tumor growth caused by Rh2E2 on LLC-1 xenograft mouse model via oral administration. C57/BL mice were subcutaneously inoculated with 2 × 106 LLC-1 mouse lung cancer cells. The administration of Rh2E2 by either IP or oral feeding was initiated when the tumor volume reached 50 mm3. The tumor size and body weight of mice were then monitored and measured daily for consecutive 21 days. E. Study on the sub-chronic lethal dose of Rh2E2. C57/BL mice were orally administrated with 160 or 320 mg/kg of Rh2E2 for consecutive 7 days, the survival and body weight of mice were monitored and recorded. F. Test of LD50 value of Rh2E2. C57/BL mice were orally administrated with single dose 2000 mg/kg of Rh2E2, the survival rate of mice was monitored and recorded for 14 days. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to the vehicle-treated group.
