Figure 4. Proteomic analysis on the tumor tissues from Rh2E2- or vehicle-treated LLC-1 xenograft mice.
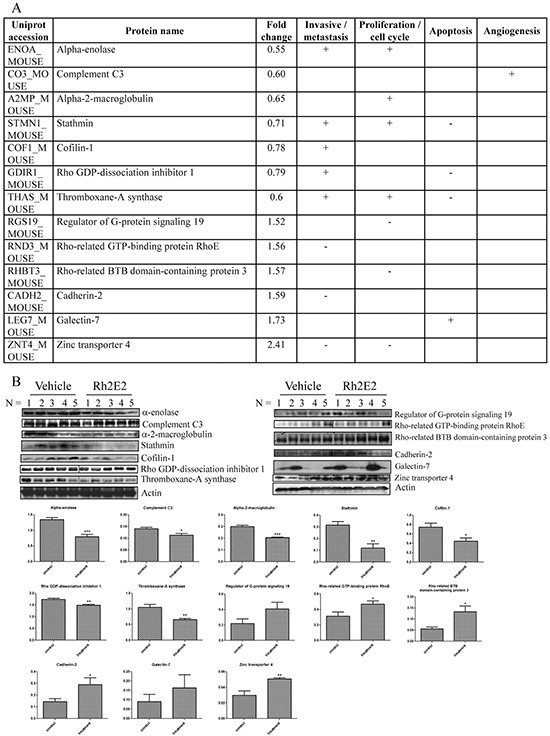
A. Rh2E2-induced differential expression of proteins were associated with invasive/metastasis, cell proliferation, apoptosis and angiogenesis of cancer cells. The comparative proteomic analyses, iTRAQ-LC-MS/MS and 2D-DIGE, were combined to maximize the identification of differentially expressed proteins. For iTRAQ, the peptide-IEF was used for fractionation before LC-MS/MS. MS/MS data was processed using Bruker Compass Data Analysis software, and the generated peak lists were submitted to MASCOT search engine against SwissProt 51.6 database. For 2D-DIGE, gels were scanned using a Typhoon 9400 (GE Healthcare) laser scanner. Image analysis was carried out with DeCyder differential analysis software 7.0 (GE Healthcare). The differentially expressed protein spots were identified by MALDI TOF/TOF. The MS data were analyzed using FlexAnalysis 3.3 (Bruker Daltonics) and the generated peak list was searched against SwissProt Mus musculus protein database (SwissProt 57.1, 462764 sequences; 163773385 residues) using in-house MASCOT Server software, version 2.3 (Matrix Science, London, UK). B. Immunoblotting validation of the identified protein targets. The protein bands intensity for corresponding protein was quantified using image J software. All quantitative data were given as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using the non-paired Student's t-test (GraphPadPrism, GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, US) to compare means. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
