Figure 6. Disrupting PD-L1/PD-1 binding using blocking antibodies markedly induced an increase in multiple immune effector molecules.
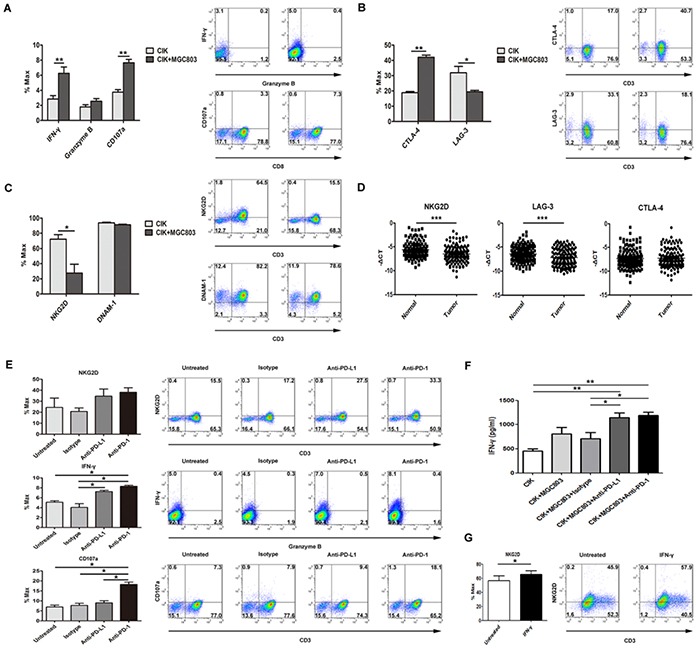
A. IFN-γ and CD107a, as direct measurements of cytotoxicity of CIK cells against tumor cells, as well as granzyme B, were observed by the co-incubation at E:T ratio of 5:1, along with the detection for a potentially responsive phenotype in terms of the co-inhibitory molecules, CTLA-4 and LAG-3 (B), and the activating receptors, NKG2D and DNAM-1 (C). D. Gastric clinical specimens were examined for analyzing the difference in the mRNA levels of these functional receptors between the gastric cancer samples and matched adjacent normal samples, and statistical significance was determined by paired t test. E. Associated immune-promoting molecules, IFN-γ and CD107a, accompanied with NKG2D levels, were examined after PD-L1/PD-1 pathway blockade using indicated antibodies (20μg/ml), among the test groups and the control groups (indicated as untreated group and isotype antibody group). F. 5×105 CIK cells were co-cultured in triplicate with 1×105 tumor cells in 500 μl culture medium per well in a 48-well-plate. Anti-PD-L1 and anti-PD-1 together with isotype antibody (20μg/ml) were separately added into each well. After 48 h, the levels of IFN-γ in the supernatants were evaluated by ELISA. G. Using the same co-culture condition described above, changes of NKG2D levels were observed with the direct adding of IFN-γ cytokine. Results represent three independent experiments and are shown as Mean±SEM (* means P<0.05, ** means P<0.01, and *** means P<0.001).
