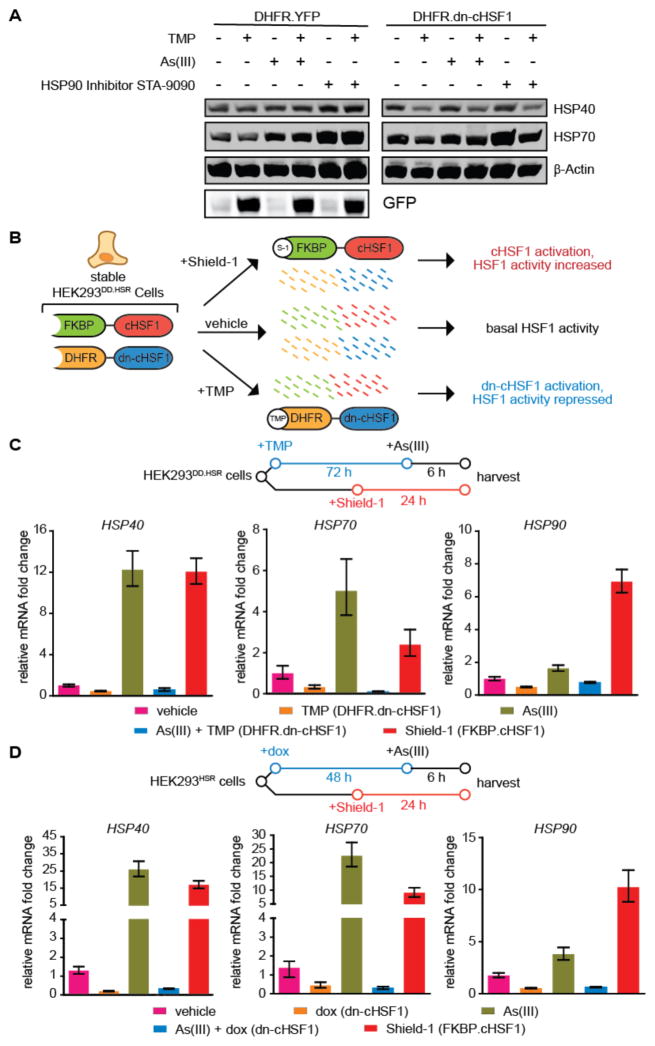
Figure 5. Inhibition and activation of HSF1 with orthogonal small molecules in a single population of HEK293 cells.
(A) Immunoblot showing the depletion of cellular chaperones upon chronic activation of DHFR.dn-cHSF1 by treatment with TMP (10 μM; 72 h).
(B) Illustration showing the incorporation of both DHFR.dn-cHSF1 and FKBP.cHSF1 into a single cell line.
(C) qPCR analysis of HSF1 target genes in HEK293DD.HSR cells expressing both TMP-regulated DHFR.dn-cHSF1 and FKBP.cHSF1. Cells were treated with TMP (10 μM; 78 h), Shield-1 (1 μM; 24 h), arsenite (100 μM; 6 h), or pre-treated with TMP (10 μM; 72 h) followed by arsenite (100 μM; 6 h).
(D) qPCR analysis of HSF1 target genes in HEK293HSR cells expressing both dox-regulated dn-cHSF1 and FKBP.cHSF1. Cells were treated with dox (1 μg/mL; 54 h), Shield-1 (1 μM; 24 h), arsenite (100 μM; 6 h), or pre-treated with dox (1 μg/mL; 48 h) followed by arsenite (100 μM; 6 h).
All qPCR data are reported as the mean ±95% confidence interval relative to vehicle-treated HEK293T-REx cells.