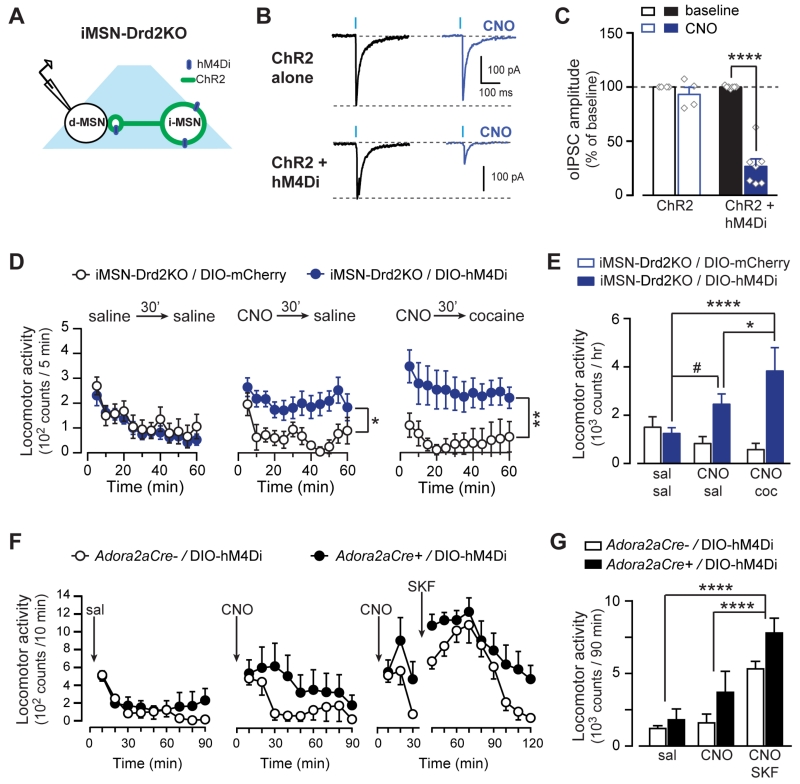
Figure 7. Activation of Gi/o signaling in iMSNs rescues the acute cocaine locomotor response.
A, Schematic of experimental configuration. B, Representative oIPSC traces and the effect of CNO in iMSN-Drd2KO mice expressing ChR2 alone or ChR2 + hM4Di in iMSNs. C, Effect of CNO (1 μM) on oIPSC amplitude as percent of baseline in iMSN-Drd2KO mice expressing ChR2 (open, n = 7) or ChR2 + hM4Di (filled, n = 5). D, Time course of the locomotor activity following saline (left), CNO (1 mg/kg, middle) or CNO followed by cocaine (15 mg/kg, right). E, Locomotion during 1 hour after sal/sal, CNO/sal, and CNO/cocaine administration for iMSN-Drd2KO mice expressing hM4Di (blue) or mCherry (white) in iMSNs. F, Time course of the locomotor activity following saline (left), CNO (1 mg/kg, middle) or CNO followed by SKF81297 (2.5 mg/kg, right). E, Locomotion during 1 hour after saline, CNO, and CNO+ SKF81297 administration for control mice expressing hM4Di (black) or not (white). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. ****p < 0.0001, #p = 0.058. All data expressed as mean ± s.e.m.