Figure 6.
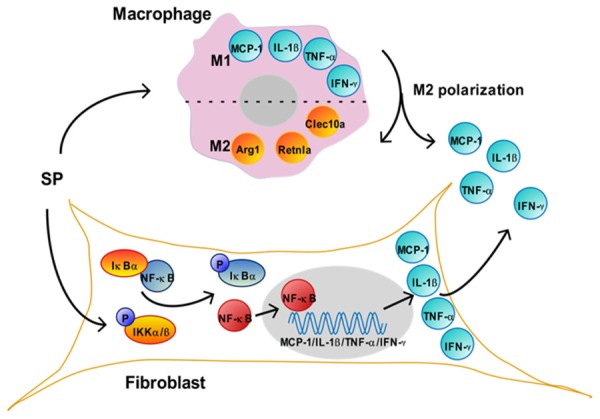
Mechanism of SP in the co-culture system. SP treatment induces the migration of macrophages to fibroblasts and M2 polarization. The markers for M1 macrophages, including MCP-1, IL-1β, TNF-α and IFN-γ, are released by macrophages during the polarization, thus helping to increase the concentration of these factors in the medium. Accordingly, the markers for M2 macrophages, including Arg1, Retnla and Clec10a are up-regulated.In fibroblasts, SP induces the phosphorylation of IKKα/β, which degrades IκBα, thus releasing and activating NF-κB. The activated NF-κB is translocated to the nucleus (grey), where it binds to MCP-1, IL-1β, TNF-α or IFN-γ, and activates the transcription of these genes. These up-regulated cytokines in fibroblast are released to the co-culture medium, which also help to increase their concentration in the medium. SP, substance P. MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. IL-1β, interleukin-1 beta. TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha. IFN-γ, interferon gamma. Arg1, arginase 1. Clec10a, c-type lectin domain family 10, member A. Retnla, resistin-like molecule alpha. IκBα, inhibitor of NF-κB alpha. IKKα/β, IκB kinase alpha/beta. NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B.
