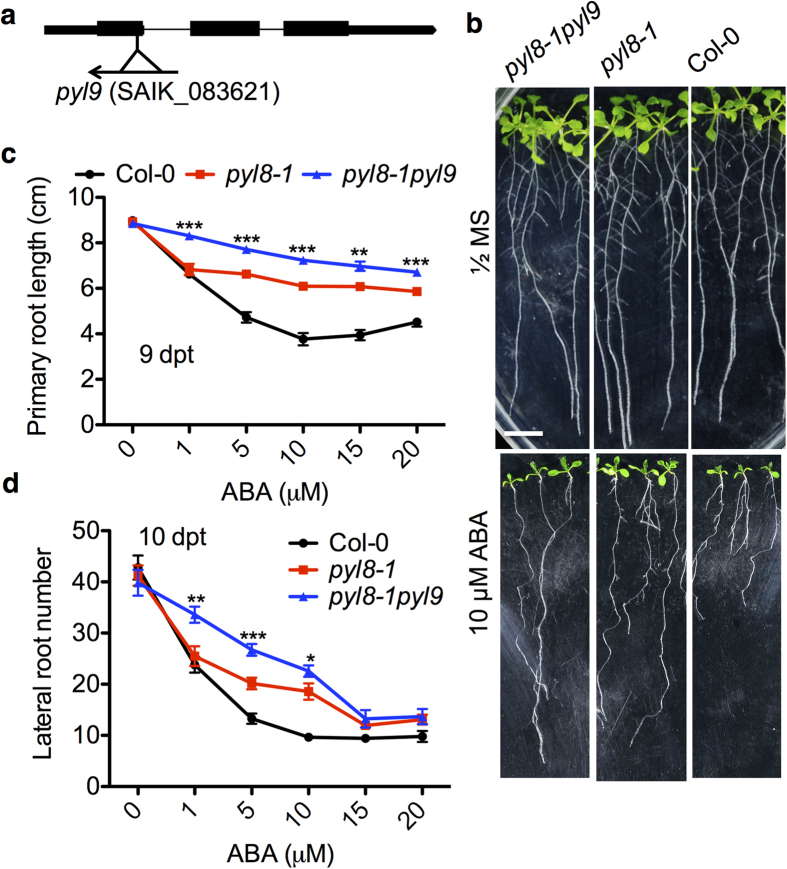
Figure 1. The primary root and lateral root formation of pyl8-1pyl9 double mutant are more insensitive upon ABA treatment.
(a) A schematic diagram of T-DNA insertions in the PYL9 gene. The T-DNA insertion in the pyl9 mutant is inserted in exon, which is presented as closed box. (b) Root architecture of Col-0, pyl8-1 and pyl8-1pyl9 mutants under ABA treatment. Root architecture of seedlings was documented at 9 dpt (days post transfer). Seedlings were transferred at 4 dpg (days post germination) to the control medium (1/2 MS, 1% sucrose) or medium with 10 μM ABA. Bar, 1 cm. (c,d) The primary root length and lateral root number of Col-0, pyl8-1 and pyl8-1pyl9 mutants were documented with different concentrations of ABA. The concentrations of ABA in the medium are as indicated. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (n = 25 seedlings, 5 independent experiments). Asterisks indicate comparison between pyl8-1 and pyl8-1pyl9. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t test. P-values were adjusted for multiple comparisons by “Benjamini & Hochberg” method. Primary root length and lateral root number of pyl8-1 (at 5 μM, 10 μM, 15 μM, 20 μM) and pyl8-1pyl9 (at all ABA concentrations) were significantly larger than Col-0, P < 0.05.