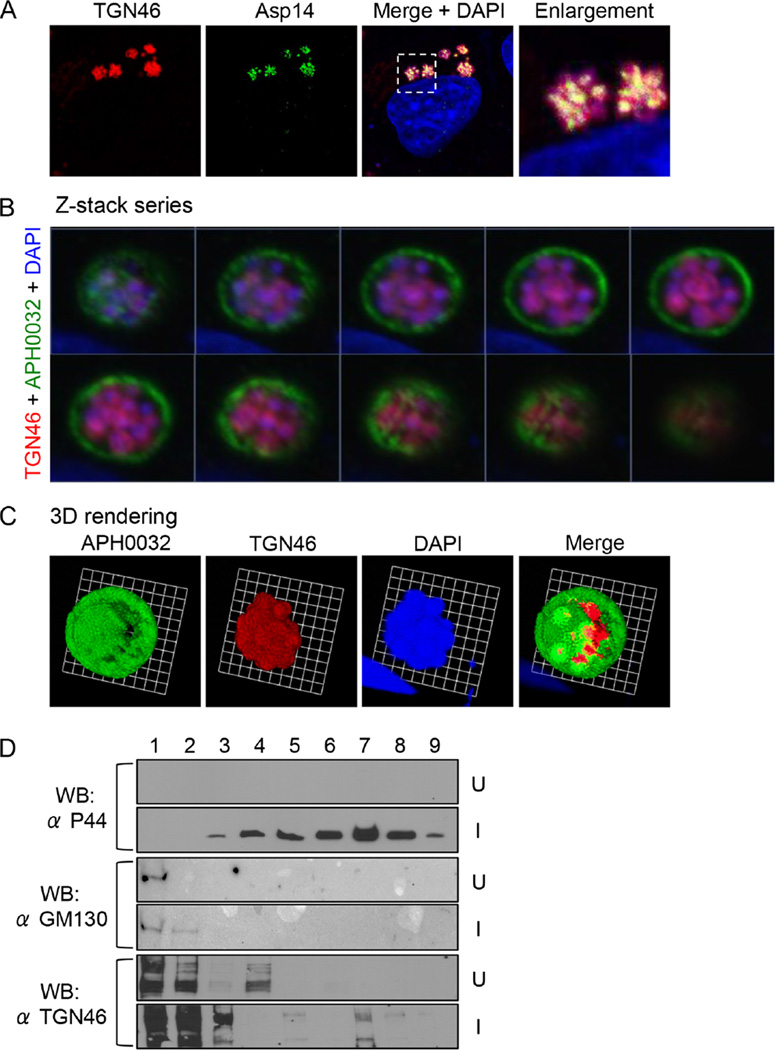
Fig. 3.
The ApV localizes adjacent to the Golgi apparatus, and TGN-derived vesicles are delivered into the ApV lumen where they associate with A. phagocytophilum organisms.
A. TGN46 signal colocalizes with intravacuolar bacteria. A. phagocytophilum-infected cells were screened with antibodies against TGN46 and Asp14 and examined by LSCM. The region that is demarcated by a hatched-line box is magnified in the enlargement panel.
B. Z-stack series shows TGN46 within the ApV. A. phagocytophilum-infected RF/6A cells were screened with antibodies against TGN46 and APH0032. Successive focal planes of a representative A. phagocytophilum vacuole are presented.
C. 3D rendering of the Z-stack series presented in B shows TGN46-positive vesicles encasing individual A. phagocytophilum organisms within the vacuole. These 3D images are also presented in Movie S2.
D. TGN46 cofractionates with A. phagocytophilum organisms. Uninfected (U) or A. phagocytophilum-infected HL-60 cells (I) were homogenized, and the post-nuclear supernatants were subjected to density gradient centrifugation. Successive 1 ml aliquots were analysed by Western blot (WB) using antibodies against TGN46, GM130 and A. phagocytophilum major surface protein, P44. Results shown are representative of three experiments with similar results.