Fig. 3.
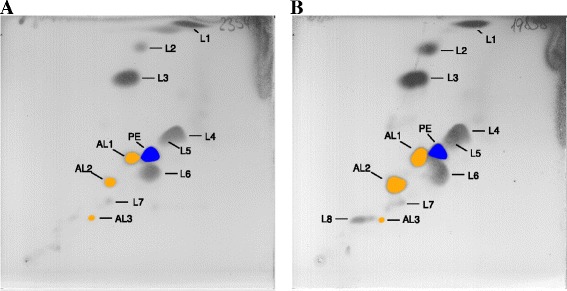
Polar lipids profiles of G. echinicola DSM 19838T and G. portivictoriae DSM 23547T. The polar lipids were extracted using a modified method of Bligh and Dyer [55] (see Tindall [56]) and separated by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography using the solvents chloroform/methanol/water (65:2:4, by vol.) in the first dimension and chloroform/methanol/acetic acid/water (80:12:15:4, by vol.) in the second dimension at 25 °C, as described by Tindall et al. [21]. For identification of the total polar lipids plates were sprayed with molybdatophosphoric acid (5 % in ethanol) and specific spray reagents used to detect the functional head groups of the lipids, as described by Tindall et al. [21]. PE, phosphatidylethanolamine (blue, phospholipid); AL, amino lipid (yellow, amino lipid); L, polar lipid
