Fig. 2.
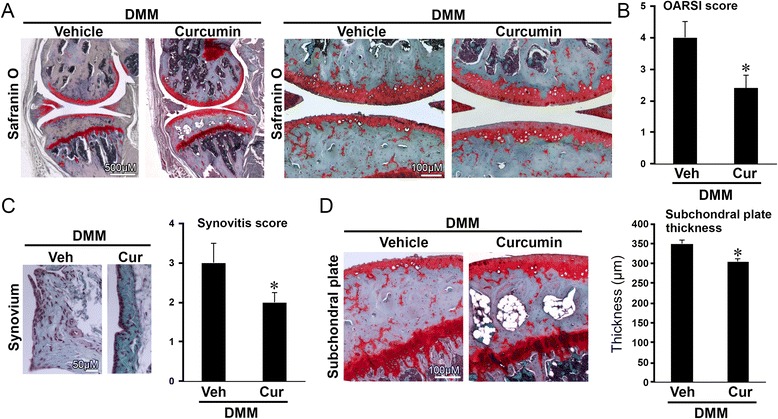
Oral administration of curcumin slowed progression of post-traumatic osteoarthritis in mice. Mice with destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) were treated daily with curcumin (Cur) or vehicle via oral gavage. Mice with DMM treated with curcumin exhibited improved Safranin O staining (a), lower Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) scores (b), and reduced synovitis (c) and subchondral plate thickness (d) at 8 weeks following surgery, compared to mice with DMM that were treated with vehicle (Veh). *P < 0.05, t test, n = 8/group. Representative histologic images are shown
