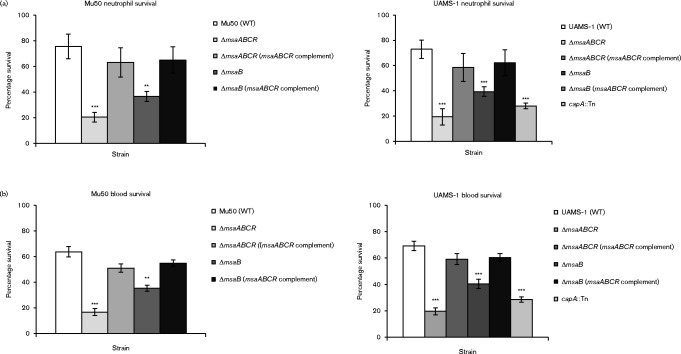
Fig. 3.
Survival assays were performed using two different methods. Bacterial cells were mixed with freshly isolated human neutrophils to measure their survival rates against phagocytosis (a). Bacterial cells were mixed with heparinized human whole blood to measure their survival rates in the presence of complementing proteins (b). Results are presented as percentages of surviving bacterial cells relative to the control, which contained water instead of neutrophils (a) or by comparing the direct count of bacteria added to the total inoculum with the total c.f.u. enumerated, corrected by any dilution factor (b). Results represent the means of three independent experiments. Error bars represent se. Student's unpaired t-test was used to compare the results of wild-types to their respective mutants. The results are displayed with asterisks using the following P value cut-offs: ** P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.