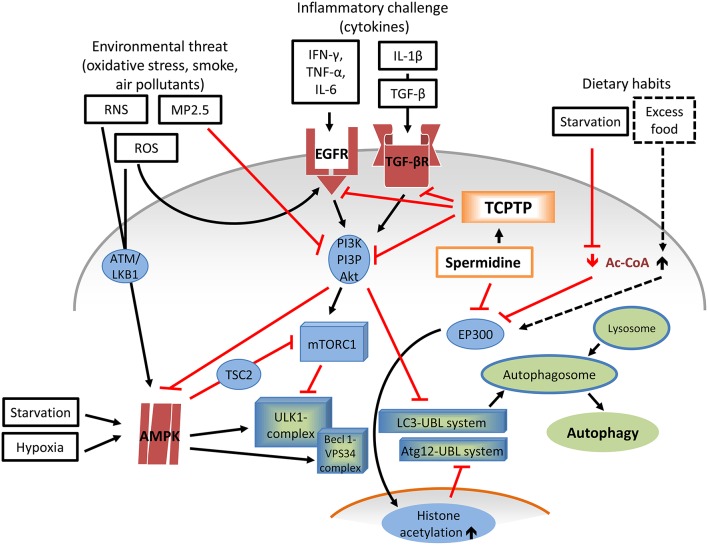
Figure 4.
Role of Spermidine-TCPTP in the complex dynamics of pro- and anti-autophagic factors. Autophagy requires the coordinated activation of multiple factors. Several Atg proteins are recruited within the ULK1 complex during vesicle nucleation and within the ubiquitin-like conjugation systems Atg12-UBL and LC3-UBL during phagophore elongation, and completion. The main autophagy repressor, mTORC1, exerts its inhibitory action by phosphorylating ULK1. mTOR interacts with the proline-rich Akt, newly synthesized in the PI3K/PI3P/Akt pathway, downstream of EGFR, and TGF-βR signaling, which in turns responds (inter-alia) to cytokines such as IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β/TGF-β. A mTORC1 antagonist and autophagy promoter is AMPK. Upon activation from non-immune stress factors including starvation, hypoxia, ROS (e.g., , H2O2, OH.), and RNS (e.g., peroxynitrite) via ATM/LKB1, AMPK prompts autophagy. AMPK is directly involved in the formation of ULK1 complex and cooperates with Becl 1-VPS34 complexes, pro-autophagy adapters involved in nucleation of autophagosome membrane. While ROS simulate EGFR activation, other environmental stressors (e.g., MP2.5) have an opposite effect, by inhibiting PI3K/PI3P/Akt. Agonistic activity of spermidine on TCPTP would down-regulate both EGFR and TGF-βR and their downstream effectors. Yet, the prevalent, established mode of action of spermidine in autophagy entails the inhibition of EP300, leading to reduced histone acetylation (particularly histone-3), and, consequently, to Atg (particularly Atg7) expression and autophagosome elongation and closure. Spermidine activity on EP300 is similar to that exerted by low cytoplasmatic levels of Ac-CoA due to scarce nutrient availability, a situation that also activates AMPK. Ac-CoA, acetyl-coenzyme A; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; superoxide anion; H2O2; hydrogen peroxide; OH., hydroxyl radical; PM2.5, particulate matter 2.5; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6, interleukin-6;, IL-1β, interleukin-1β; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; TGF-βR, transforming growth factor β receptor; ULK1/2, UNC-51-like kinases 1/2; ATM ataxia telangiectasia mutated kinase; LKB1, upstream kinase of AMPK; AMPK adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; TSC2, tuberous sclerosis 2; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin type-1 complex; EP300, E1A-binding protein p300; Beclin 1-VPS34 complex, Beclin 1-ATG14L; VPS34, class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Atg autophagy related proteins; ULK1-complex, Atg13-FIP200-Atg101-Atg14L conjugation system; FIP200, FAK-family interacting protein of 200 kDa; Atg12-UBL system, Atg5-Atg12-Atg10-Atg16-Atg7 pathway; LC3-UBL system, LC3-Atg3-Atg4-Atg7-PE pathway; LC3, microtubule-associated protein light chain 3; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; HAT, histone acetyltrasferase.