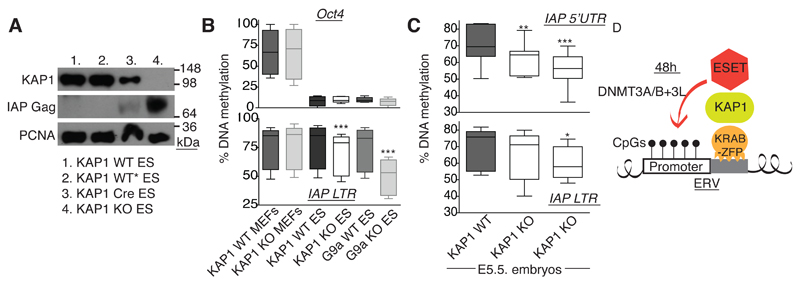
Fig. 6. KAP1 shapes DNA methylation of endogenous retroviruses in ES cells and embryos.
A) KAP1 knockout in ES cells leads to an accumulation of IAP GAG p73 expression. ES cells with loxP-flanked Kap1 untreated (1.) or treated with 4-OHT (2.) or transduced with 4-OHT-inducible Cre, without (3.) or with 4-OHT (4.). Cells were harvested 4 days post 4-OHT treatment. B) KAP1 WT and KO ES cells were analysed for DNA methylation of global IAP LTRs (bottom). Methylation of the Oct4 promoter (top), G9a KO ES cells and KAP1 KO MEFs were used as controls. P values for the IAP LTR: KO MEFs were not different to WT MEFs (p=0.2186); KAP1 KO ES cells were significantly different to WT (p=0.0008) and G9a KO ES were significantly different to WT (p=0.0002). C) Kap1 heterozygous mice (C57BL/6) were crossed and embryos dissected at E5.5 to measure DNA methylation of endogenous IAPs using primers either in the 5’UTR (top) or LTR (bottom). Here two knockouts and one WT embryo were analysed. Top: p=0.0059 and 0.0006 respectively. Bottom: p=0.1613 (not significant) and 0.0493 respectively (paired one-tailed t tests). D) Summary model: KRAB-ZFPs, KAP1 and ESET are necessary for de novo methylation of ERVs, occurring within 48 hours. This process is sequence-specific and takes place in ES cells and embryogenesis.