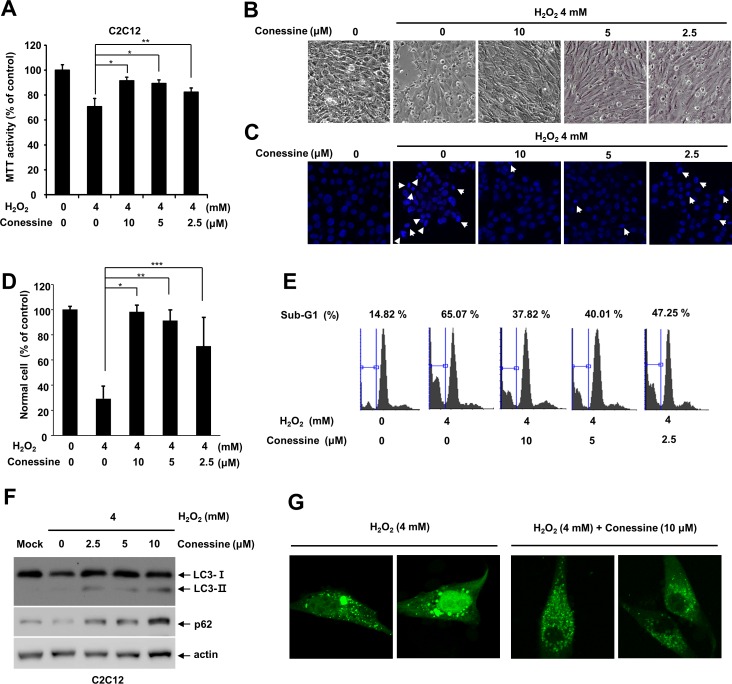
Fig 5. Conessine treatment protects C2C12 myoblast cells from H2O2-induced cell death.
(A) Conessine treatment interferes with H2O2-induced C2C12 cell death. C2C12 cells were treated with the indicated concentration of conessine, followed by H2O2 treatment (4 mM) for 24 h. Relative cell viability was measured by MTT assay. Control versus conessine treatment, * P < 0.01; ** P <0.05 (B) Cellular morphological changes were observed under a phase contrast microscope. (C, D) Apoptotic cells were quantified by counting DAPI-stained nuclei, and apoptotic cells showed nuclei and chromatin condensation. The number of normal cells were shown in graph. At least 160 cells were counted in each samples. Control versus conessine treatment, * P < 0.00005; ** P <0.0005; *** P<0.05. (E) Conessine decreased the sub-G1 cell population, which was induced by H2O2 treatment. C2C12 cells were treated with conessine and H2O2, and the cell cycle was analyzed with flow cytometry. (F) Conessine attenuates H2O2 induced autophagy. C2C12 cells were sequentially treated with conessine and H2O2, and the cell lysates were subject to Western blot with the indicated antibodies. (G) Conessine alleviates H2O2-induced excessive autophagy. C2C12 cells were transfected with GFP-LC3 and sequentially treated with conessine and H2O2. The cells were analyzed by confocal microscopy.