FIGURE 1.
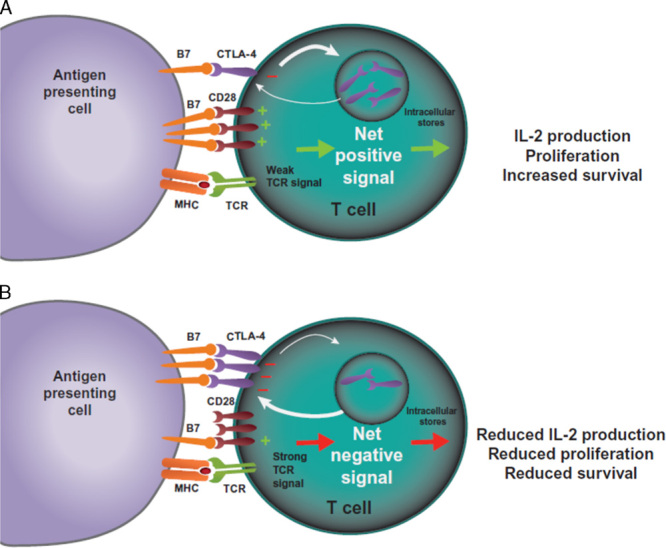
CTLA-4-mediated inhibition of T cells. T cells are activated when TCRs bind antigen displayed in the MHC on antigen-presenting cells in concert with CD28:B7-mediated costimulation. A, In the case of a weak TCR stimulus, CD28:B7 binding predominates, resulting in a net positive activating signal and IL-2 production, proliferation, and increased survival. B, In the case of a strong TCR stimulus, CTLA-4 expression is upregulated by increased transport to the cell surface from intracellular stores and decreased internalization. CTLA-4 competes with CD28 for binding of B7 molecules. Increased CTLA-4:B7 binding can result in a net negative signal, which limits IL-2 production and proliferation, and limits survival of the T cell. CTLA-4 indicates cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated antigen 4; IL-2, interleukin-2; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TCR, T-cell receptor.
