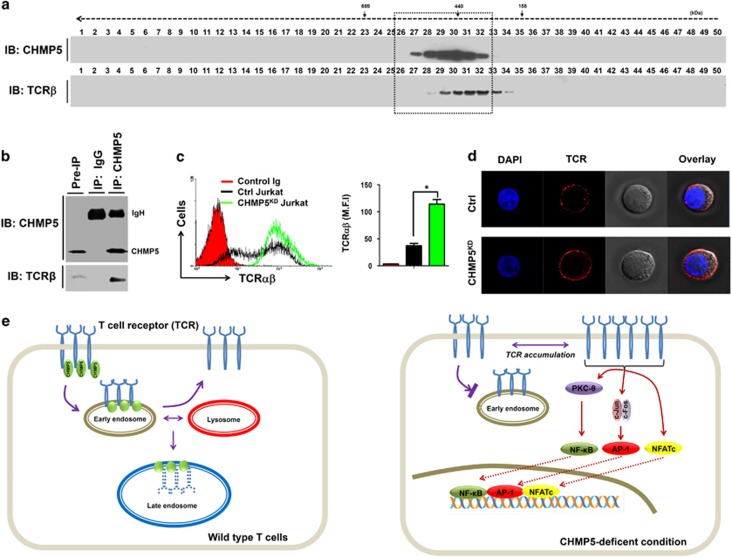
Figure 6.
CHMP5 regulates the TCR expression on the surface. (a) Cell lysates from Jurkat T cells were prepared and fractionated through a Superose6 10/300 GL column, as described in Materials and methods section. Each fraction (40 μl) was analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with the indicated antibody to anti-CHMP5 or anti-TCRβ. (b) Cell lysates from Jurkat T cells were prepared and an immunoprecipitation assay was performed with anti-CHMP5 antibody or IgG antibody as a negative control. The interaction between CHMP5 and TCRβ was evaluated by western blotting. (c) Control (Ctrl) and CHMP5KD Jurkat cells were stained with control Ig or PE-conjugated TCRαβ antibody and then analyzed by flow cytometry. The TCR expression was represented by mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). *P<0.01. (d) Ctrl and CHMP5KD Jurkat cells were stained with PE-conjugated TCRαβ antibody and immunofluorescence microscopy analysis was performed. (e) A mechanistic model of the role of CHMP5 in TCR expression. Left: In wild-type cells, CHMP5 is associated with TCR and involved in the regulation of constitutive T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) recycling to the cell surface. Right: TCR recycling is impaired in deficiency of CHMP5 and TCR expression increases on the cell surface. Upon TCR stimulation, the accumulated TCRs are functionally induced to activate TCR-induced transcriptional factors, such as NF-κB, AP-1 and NFAT, leading to gene expression.