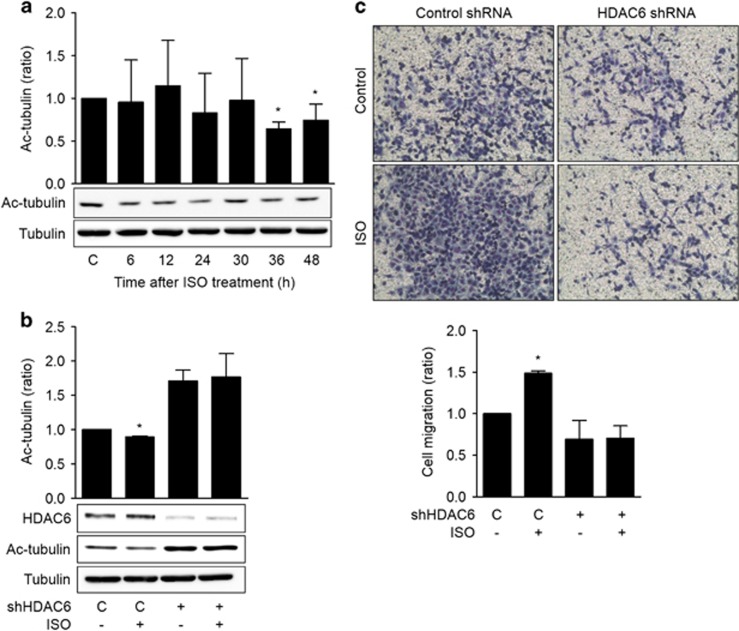
Figure 2.
Isoproterenol increases the migration of H1299 lung cancer cells via the HDAC6-dependent deacetylation of α-tubulin. (a) Effects of isoproterenol on the acetylation of α-tubulin. H1299 cells were treated with 20 μM isoproterenol (ISO), and the levels of acetylated α-tubulin (Ac-tubulin) and total α-tubulin at the indicated time points were assessed by western blotting. (b) Effects of HDAC6 knockdown on the isoproterenol-induced deacetylation of α-tubulin. H1299 cells in 100-mm dishes were transfected with shRNA targeting HDAC6 or control shRNA (10 μg) and incubated for 24 h. Then the cells were treated with 20 μM isoproterenol for an additional 48 h prior to harvesting for western blotting analysis. (c) Effects of isoproterenol on the migration of H1299 lung cancer cells. A transwell migration assay was performed. In brief, H1299 cells were transfected with shRNA targeting HDAC6 or control shRNA, and the cells were seeded onto the upper chamber containing 20 μM isoproterenol. After 16 h, the migrated cells were fixed and stained, and representative photographs (× 100 magnification) of the migrated cells are presented. The migrated cells were counted in five different microscopic fields, and the averages were calculated. The values presented are the means±s.ds. of three independent experiments. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences from the isoproterenol-untreated control (P<0.05, Mann–Whitney U-test).