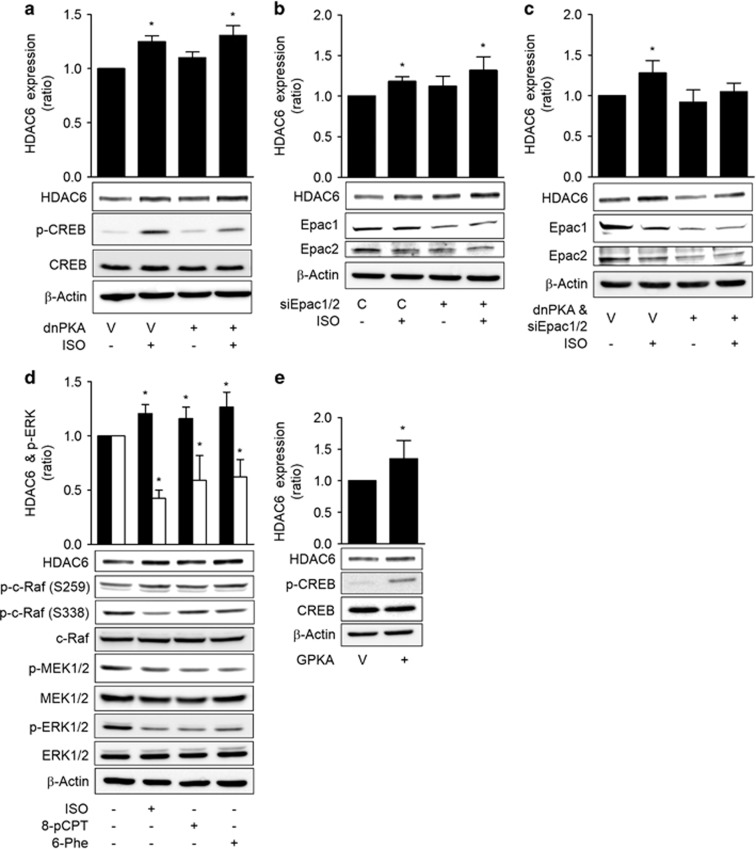
Figure 4.
Isoproterenol inhibits c-Raf via the PKA and Epac pathways. (a) Effects of PKA inhibition on the isoproterenol-induced increase in HDAC6 expression. (b) Effects of Epac knockdown on the isoproterenol-induced increase in HDAC6 expression. (c) Effect of simultaneous PKA inhibition and Epac knockdown on the isoproterenol-induced increase in HDAC6 expression. (d) Effects of Epac- and PKA-selective agonists on HDAC6 expression and the c-Raf-MEK-ERK pathways. (e) Effects of PKA activation on HDAC6 expression. H1299 cells were transfected with dominant-negative PKA (dnPKA), Epac1 siRNA, Epac2 siRNA or scrambled control siRNA, incubated for 24 h and then treated with 20 μM isoproterenol (ISO) for 48 h prior to western blotting analysis. The H1299 cells were also treated for 48 h with 20 μM ISO, 20 μM 8-pCPT-2′-O-Me-cAMP (8-pCPT) or 30 μM N6-phenyl-cAMP (6-Phe) or transfected with the catalytic subunit of PKA (GPKA) or EGFP vector for 48 h. Then HDAC6 expression was analyzed by western blotting. Filled bar represents HDAC6 expression and empty bar represents p-ERK. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences from the respective control cells (P<0.05, Mann–Whitney U-test).