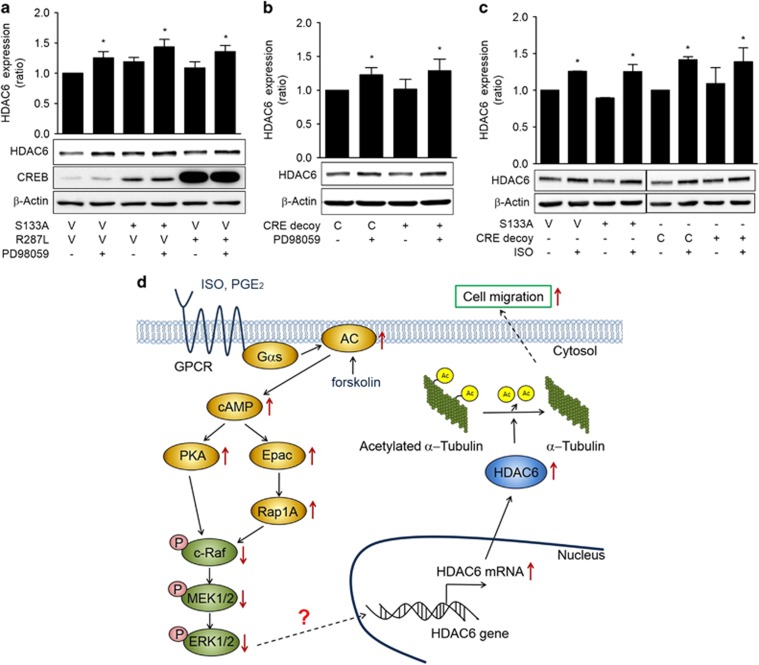
Figure 6.
Inhibition of c-Raf-MEK-ERK pathways increases HDAC6 expression in a CREB-independent manner. (a) Effects of dominant-negative CREB on PD98059-induced HDAC6 expression. (b) Effects of CRE decoy oligonucleotides CREB on PD98059-induced HDAC6 expression. (c) Effects of CRE decoy oligonucleotides CREB on isoproterenol-induced HDAC6 expression. H1299 cells were transfected with dominant-negative CREBs (S133A, R287L), respective control vectors (V) or CRE decoy and control (C) oligonucleotides and then incubated for 24 h. The cells were then treated with 20 μM PD98059 (PD), isoproterenol (ISO) or dimethyl sulfoxide for 48 h before western blotting analysis. (d) A suggested mechanism by which isoproterenol increases HDAC6 expression in human lung cancer cells. Isoproterenol increases HDAC6 expression via the PKA- and Epac-mediated inhibitions of c-Raf-MEK-ERK, which result in increased cell migration. The solid lines indicate proven signaling pathways, and the dotted lines indicate potential signaling pathways. GPCR, G-protein-coupled receptor. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences from the respective control cells (P<0.05, Mann-Whitney U-test).