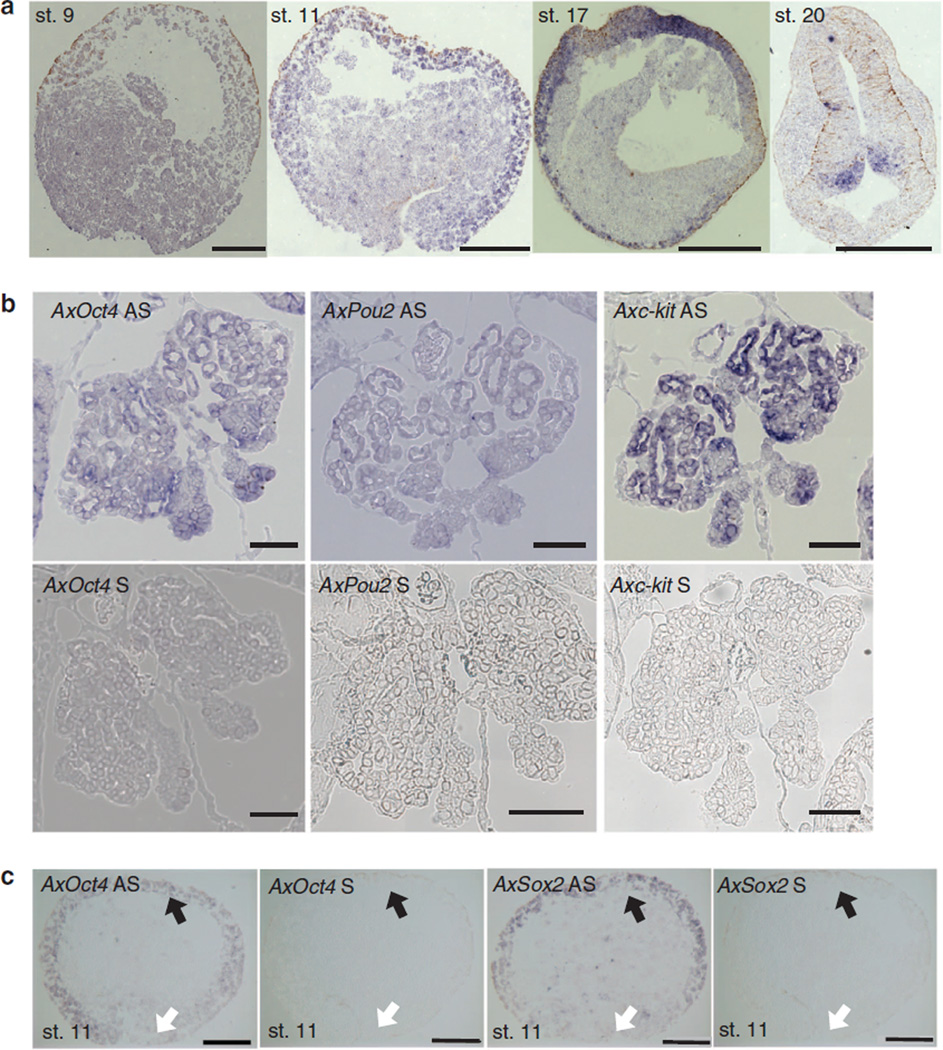
Figure 2. Localization of AxOct4, AxPou2 and AxSox2 in axolotl embryos.
(a) Expression of AxPou2 mRNA during embryonic development of axolotl. AxPou2 showed a weak expression signal in stage-9 blastula-stage embryos. AxPou2 was expressed in the ectoderm of animal cap and blastopore lip of a stage-11 (early gastrulation) embryo and in the ectoderm of stage-17 neurula-stage embryos. At stage 20, a large signal is seen in the neural tube in the hindbrain region (right) during neurulation and in the hindbrain in somite-stage embryos. In situ hybridization was performed on paraffin section (10-µm thick). Image was taken in bright field (NA 0.8); scale bar, 500 µm. st, stage. (b) AxOct4, AxPou2 and Axc-kit mRNA are present in gonia during development of axolotl. Sense control probes show no background signal. The negative control using the sense probe is indicated with S, and the specific signal from the antisense probe is labelled with AS. In situ hybridization was performed on paraffin section (10 µm thick) of 3-cm axolotl larvae. Image was taken in bright field (NA 0.8); scale bar, 100 µm. (c) AxOct4 and AxSox2 RNA in situ hybridization in a stage-11 axolotl embryo (38.5h post fertilization). The negative control using the sense probe is indicated with S, and the specific signal from the antisense probe is labelled with AS. The black arrows mark the axolotl animal cap (equivalent to the mouse epiblast); the white arrows mark the axolotl blastopore lip (equivalent to the mouse primitive streak). Scale bars, 500 µm.