Fig. 4.
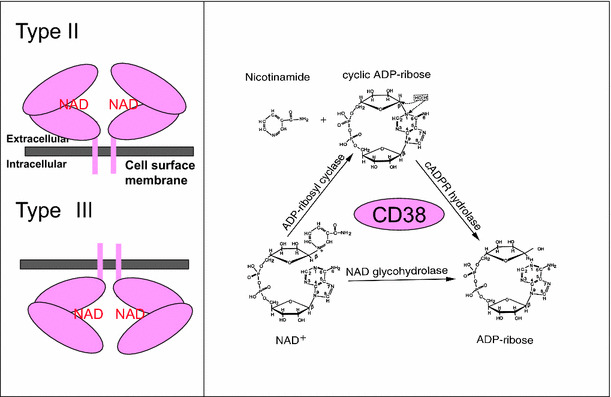
Membrane topology and enzyme reaction of CD38. CD38 (pink oval) usually forms a dimer. β-NAD+ binds to the central catalytic site of CD38. The large C-terminal part is located in the extracellular space, as the type II transmembrane protein, or intracellular space as the type III transmembrane protein, according to Lee and colleagues [66, 67]. CD38 has three enzymic activities. CD38 catalyzes formation of cyclic ADP-ribose from β-NAD+ by cleaving nicotinamide. cADPR is hydrolyzed to form ADP-ribose. β-NAD+ also has NAD+ glycohydrolase activity to form ADP-ribose from β-NAD+ in one step. The scheme of enzyme activity is modified from Lee [50]
