Fig. 3.
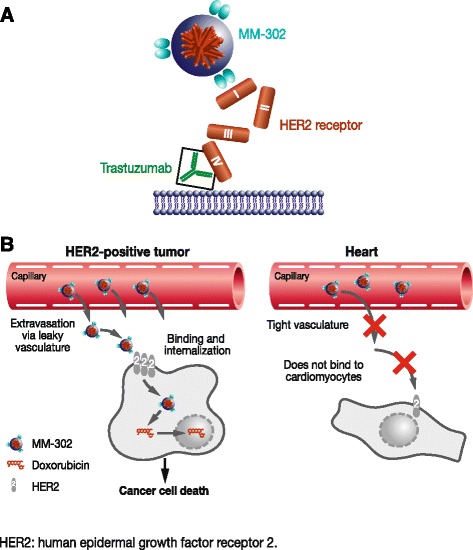
Mechanism of action of MM-302. a MM-302 binds to HER2 extracellular subdomain I, whilst trastuzumab binds to subdomain IV. b MM-302 remains in circulation for long periods of time, providing an opportunity to accumulate in tumors via leaky vasculature. Once in the tumor microenvironment, MM-302 binds specifically to tumor cells that overexpress HER2 (>200 000/cell) and undergoes receptor-mediated endocytosis, releasing doxorubicin inside the cell. By contrast, the vasculature of the heart is more intact and prevents extravasation out of the blood vessels. Furthermore, cardiomyocytes express HER2 below the threshold required for uptake; therefore, MM-302 does not inhibit HER2-mediated signaling in cardiomyocytes [34, 35]
