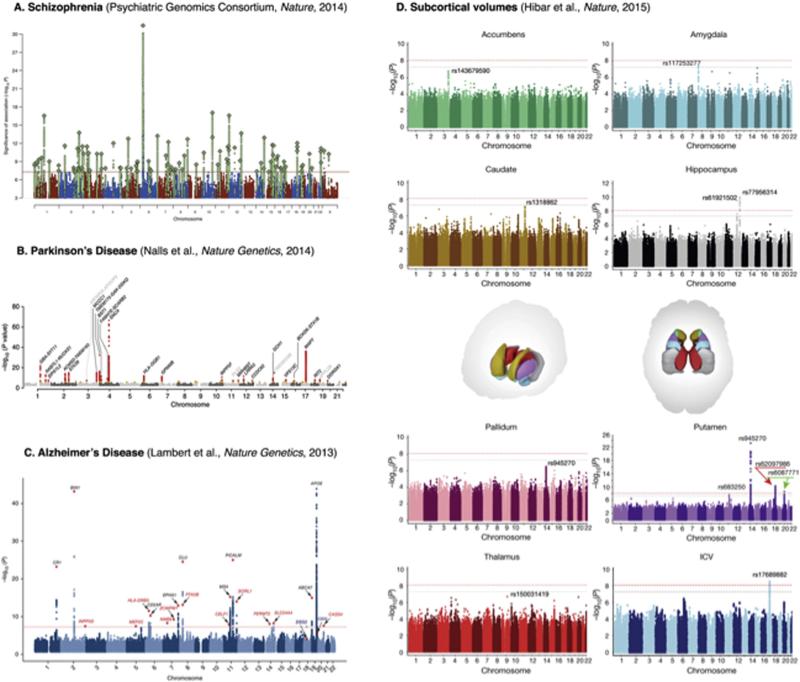
Fig. 1.
Recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of brain disorders and brain structure. Part A shows the Manhattan plot from a 2014 Nature meta-analysis conducted by the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. The genetic variants are presented on the x-axis, and the height of the dots shows the strength of association between each genetic variant and schizophrenia. A negative log p-value scale is used: higher points denote stronger associations. The group identified 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci in a sample of 34,241 cases and 45,604 controls (red line = genome-wide significance level, conventionally set at p = 5×10–8; green SNPs = polymorphisms in linkage disequilibrium with index SNPs (diamonds), which indicate independent genome-wide significant signals). Part B 26 loci significantly associated with risk of Parkinson's Disease (Nalls et al., 2015), in 13,708 cases and 95,282 controls (red SNPs = genome-wide significant signals). Part C 19 loci significantly associated with risk of AD, in a sample of 17,008 cases and 37,154 controls (Lambert et al., Nature Genetics, 2013; genes identified by previous GWAS are shown in black; newly associated genes in red; red diamonds indicate SNPs with the smallest overall p-values in the analysis). Part D shows genome-wide associations for eight subcortical structures, conducted by the ENIGMA consortium in 30,717 individuals from 50 cohorts worldwide (Hibar et al., Nature, 2015). This study identified five novel genetic variants associated with differences in the volumes of the putamen and caudate nucleus and stronger evidence for three previously established influences on hippocampal volume (see Stein et al., Nature Genetics, 2012) and intracranial volume (see Ikram et al., Nature Genetics, 2012). Each Manhattan plot in Part D is color-coded to match its corresponding subcortical structure, shown in the middle row. The gray dotted line represents genome-wide significance at the standard p = 5×10–8; the red dotted line shows a multiple-comparison corrected threshold of p = 7.1 × 10–9. [Images are reproduced here with permission from MacMillan Publishers Ltd (Nature Genetics, 2012 & 2013; Nature, 2014 & 2015) and with permission from the corresponding authors.]